2020/1/26 アメリカ合衆国・マサチューセッツ工 科大学(MIT)
・ MIT と米国立再生可能エネルギー研究所(NREL)が、シリコン太陽電池のセルを薄くすることで太陽光発電コストを低減する、新たなアプローチについて報告。太陽電池製造技術の拡張に向けたロードマップを提供する。
・太陽光パネルのコストは過去数年間で下落しており、専門家の予想を超える速度で導入が進んでいるが、さらにコストが削減できる部分の特定が困難。
・薄型のシリコン電池は、特に十年ほど前のシリコン供給不足による価格高騰以降に開発が進んだが、シリコンウェハーは脆く壊れやすいため、製造プロセスにおける損失が多大なことや、エネルギー変換効率が低いこと等の課題あり。
・「テクノエコノミック」と表現される新アプローチでは、太陽光パネルの入手のし易さの向上において、現時点では経済的要件が技術的要件と同等の重要性を有することを強調。
・現在、世界の太陽光パネルの90%を占め、毎年約30%の産業成長率を示すシリコン太陽電池は160μ m の薄さのシリコンのウェハ-を使用しているが、製造方法の向上により 100μ m の薄さの実現が可能。最終的には 40μ m を下回ることで、製造に必要なシリコン量を従前の 1/4 まで低減できると考える。
・このことは、個々の太陽光パネルのコストの低減だけでなく、その製造業者の稼働能力の急速な拡張にも寄与する。ウェハーを作るためのシリコン結晶インゴット製造工場は、通常は太陽電池製造工場からは離れた場所に存在し、その建設に多大な資本と時間を要する。ウェハーをさらに薄くすることで、この問題の解決に貢献できると考える。
・ PERC セル(セル背面にパッシベーション膜を設けたもの)や他び高効率技術を含む 4 種類の太陽電池構造について、各セルの薄さと発電能力について調査し、より高度な製造プロセスを利用することで、40μ m までの薄さでは性能の低下が観られないことがわかった。効率性とウェハー薄さの関係において、効率性に変化の無い領域が、コスト低減の実現が可能な箇所と認識。
・大規模な太陽光パネル製造工場により薄いウェハーを導入するプロセスは時間とコストがかかるが、実現できればそれらを上回る便益の獲得が可能と考える。また、シリコン結晶ウェハーを直接成長させる新技術等により、15μ m 等のさらに薄いウェハー製造も可能と考える。
・かつて集積回路産業がその産業規模拡大のために実施したように、産業界の様々な主要なプレイヤーが寄り合って今後の計画と合意した規格について決定することが重要と考える。
・本研究は、米国エネルギー省(DOE)、Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology(SMART)および MIT Energy Intensive を通じた Total Energy Fellowship が一部支援した。
URL: http://news.mit.edu/2020/cheaper-solar-cells-thinner-0127
(関連情報)
Energy & Environmental Science 掲載論文(アブストラクトのみ:全文は有料)Revisiting thin silicon for photovoltaics: a technoeconomic perspective
URL: http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C9EE02452B
<NEDO海外技術情報より>

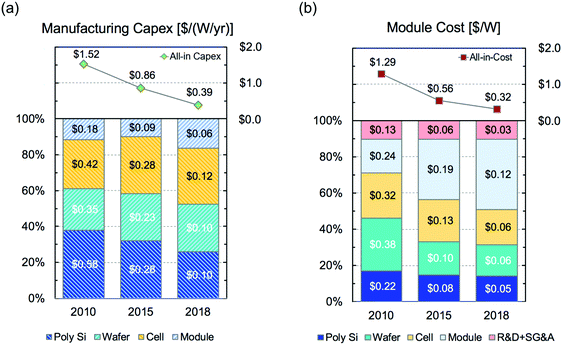
図1(a)PV製造(すなわち、ポリSiからモジュール)の設備投資と(b)2010、2015、2018年の単結晶Si PVモジュールのモジュールコスト。PV製造のサプライチェーンにおける特定の貢献は、次のように分類されます。 多結晶シリコンの生産、インゴットの成長とウェーハ、セル処理、モジュールの組み立て。 設備投資は、ワットあたりの年間製造能力で正規化された資本支出として報告されます。単位は[$ per(W per year)]です。モジュールコストは、モジュールの電力出力に正規化された生産費用として報告されます。 W]。 これらの値は、refのNRELベンチマークです。 4は、各年の世界の製造業の中央値を表しています。
Abstract
Crystalline silicon comprises 90% of the global photovoltaics (PV) market and has sustained a nearly 30% cumulative annual growth rate, yet comprises less than 2% of electricity capacity. To sustain this growth trajectory, continued cost and capital expenditure (capex) reductions are needed. Thinning the silicon wafer well below the industry-standard 160 μm, in principle reduces both manufacturing cost and capex, and accelerates economically-sustainable expansion of PV manufacturing. In this analysis piece, we explore two questions surrounding adoption of thin silicon wafers: (a) What are the market benefits of thin wafers? (b) What are the technological challenges to adopt thin wafers? In this analysis, we re-evaluate the benefits and challenges of thin Si for current and future PV modules using a comprehensive technoeconomic framework that couples device simulation, bottom-up cost modeling, and a sustainable cash-flow growth model. When adopting an advanced technology concept that features sufficiently good surface passivation, the comparable efficiencies are achievable for both 50 μm wafers and 160 μm ones. We then quantify the economic benefits for thin Si wafers in terms of poly-Si-to-module manufacturing capex, module cost, and levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) for utility PV systems. Particularly, LCOE favors thinner wafers for all investigated device architectures, and can potentially be reduced by more than 5% from the value of 160 μm wafers. With further improvements in module efficiency, an advanced device concept with 50 μm wafers could potentially reduce manufacturing capex by 48%, module cost by 28%, and LCOE by 24%. Furthermore, we apply a sustainable growth model to investigate PV deployment scenarios in 2030. It is found that the state-of-the-art industry concept could not achieve the climate targets even with very aggressive financial scenarios, therefore the capex reduction benefit of thin wafers is advantageous to facilitate faster PV adoption. Lastly, we discuss the remaining technological challenges and areas for innovation to enable high-yield manufacturing of high-efficiency PV modules with thin Si wafers.



