2022-09-29 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
研究チームは、ロボットやウェアラブルに組み込み、人工知能を使って機能を最適化できるようにシナプス・トランジスタを設計している。
シナプス・トランジスタを用いたロボットやウェアラブル機器は、人間の脳を模倣し、その人工ニューロンを使って行動を「学習」し、適応させることができる。
このデバイスの人工ニューロンは、脳幹の最上部に位置する人間の脳の小さなセグメントである腹側被蓋野のニューロンのように動作するように設計されている。ニューロンは、神経細胞の末端にあるシナプスで神経伝達物質を放出することにより、情報の処理と伝達を行う。興奮性神経伝達物質は、他の神経細胞の活動を誘発し、記憶の強化に関連する。一方、抑制性神経伝達物質は、他の神経細胞の活動を抑制し、記憶の弱化に関連する。
脳の他のすべての領域とは異なり、腹側被蓋野の神経細胞は、興奮性神経伝達物質と抑制性神経伝達物質の両方を同時に放出することができる。シナプス・トランジスタを両方のシナプス動作で同時に動作するように設計することで、従来の集積エレクトロニクス技術に比べて必要なトランジスタの数が少なくなり、システム・アーキテクチャが単純化され、デバイスのエネルギーを節約することが可能になる。
柔らかく伸縮する生体組織をモデル化するために、研究者たちは、伸縮可能な二層半導体材料を用いてデバイスを作製し、使用中に伸びたりねじれたりできるようにした
このトランジスタは、機械的に変形でき、機能的に再構成可能でありながら、大きく伸ばしてもその機能を維持することがでる。ロボットやウェアラブルデバイスに取り付けて、その最外皮として機能させることができる。
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/engineering/story/stretchy-bio-inspired-synaptic-transistor-can-enhance-weaken-device-memories/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-022-00836-5
伸縮自在な二層膜半導体を用いた伸縮自在で再構成可能なシナプストランジスタ An elastic and reconfigurable synaptic transistor based on a stretchable bilayer semiconductor
Hyunseok Shim,Faheem Ershad,Shubham Patel,Yongcao Zhang,Binghao Wang,Zhihua Chen,Tobin J. Marks,Antonio Facchetti & Cunjiang Yu
Nature Electronics Published:29 September 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-022-00836-5
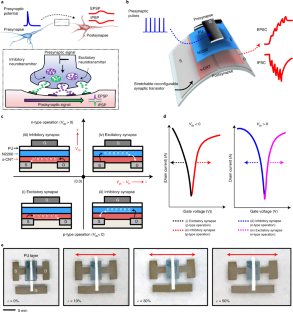
Abstract
Neurons of the ventral tegmental area of the brain contain single axon terminals that release excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters, creating reconfigurable synaptic behaviour. Artificial synaptic transistors that exhibit similar excitatory and inhibitory behaviour—and hence synaptic function reconfiguration—could provide diverse functionality and efficient computing in various applications. However, some of these applications, such as soft robotics and wearable electronics, require synaptic devices that are mechanically soft and deformable. Here we report an elastic and reconfigurable synaptic transistor that exhibits inhibitory and excitatory characteristics even under mechanical strain. The synaptic device uses a top-gated configuration and is made using a stretchable bilayer semiconductor and an encapsulating elastomer as the gate dielectric. The device exhibits memory characteristics when operating with a presynaptic pulse of only 80 mV, resulting in a low specific energy consumption. When applied to a model artificial neural network for dual-directional image recognition of the Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology dataset, a recognition accuracy of over 90% is achieved even when the transistors are stretched by 50%.



