2022-07-14 ライス大学
・ ライス大学が、単層カーボンナノチューブ(SWCNTs)の蛍光発光を利用した、歪みを検出する「スマートスキン」を開発。
・ 2012 年に開発した「歪みペンキ」をベースに、S4(strain-sensing smart skin)として知られる非接触型光学モニタリングシステムとして開発。高い歪みが不可視の脅威となる橋梁、ビル、船舶や航空機等の大面積に噴射・塗装して利用できる、次世代の非接触型の歪みモニタリング手段を提供する。
・ CNTs の蛍光発光特性を利用して圧力による表面の変形を提示する「歪みペンキ」は、近赤外波長での CNTs の蛍光発光の発見後のナノチューブの物理・化学特性調査に向けた光学機器の開発(2002 年)、分光学的歪み効果の確認(2008 年)、そして別途の CNTs フィルムによる非接触式光学歪みセンサーの開発(2004 年)の統合を経て開発に至った。
・ 歪み測定は安全性の検査に含まれ、信頼性の高さが極め点重要。「スマートスキン」は、本格的な歪み測定技術として、歪みマッピング技術で唯一商業化されているデジタル画像相関法(DIC)とも好相性。確立された既存の技術と同様の効果を提供する。
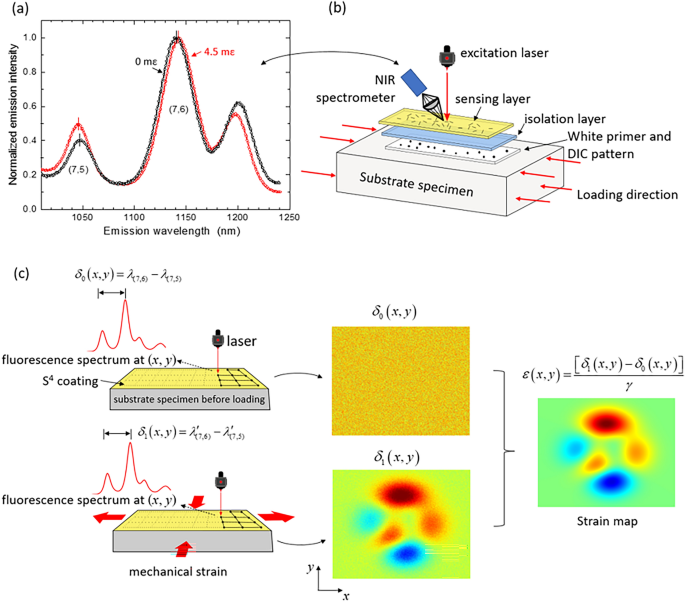
・ 「スマートスキン」は、DIC のスペックルパターンを含む不透明のプライマーコーティング底部層、透明なポリウレタン中間層、トルエンに浮かぶ個別に有機ポリマーでコーティングしたナノチューブをスプレーして作るセンシング層の 3 層構造。
・ トルエンが蒸発すると、構成部材の形状に合わせて付着するサブミクロンの薄さのセンシング層が残る。保護層を追加塗布することで数年間の作動する。歪み測定システムには、ナノチューブを励起する微小な可視光レーザーと歪みの状態を観察するポータブルな分光器によるリーダーが含まれる。
・ 穴や切り込みのある長方形のアクリル棒、歪みパターンの集約のために穴を開けたコンクリートブロックやアルミ板を使用した試験にて DIC、コンピューターシミュレーションと S4 を比較した結果、全ての場合において DIC の結果に匹敵または超越する、加圧された被検物の高分解能で正確な歪みマッピングを確認した。
・ DIC でのデータ取得は容易だが、良好な測定結果獲得にはオペレーターによる高い専門性が必要。S4 ではデータ取得が DIC と同様に容易な上、歪みマップ作成のための分析が自動的に実行される。現在、産業での利用方法を検討中。
・ 本研究は、米国海軍研究室(ONR) および米国立科学財団(NSF)が支援した。
URL: https://news.rice.edu/news/2022/strain-sensing-smart-skin-ready-deploy
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
関連情報
Scientific Reports 掲載論文(フルテキスト)
Next-generation 2D optical strain mapping with strain-sensing smart skin compared to digital image
correlation
URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-15332-1
Abstract
This study reports next generation optical strain measurement with “strain-sensing smart skin” (S4) and a comparison of its performance against the established digital image correlation (DIC) method. S4 measures strain-induced shifts in the emission wavelengths of single-wall carbon nanotubes embedded in a thin film on the specimen. The new S4 film improves spectral uniformity of the nanotube sensors, avoids the need for annealing at elevated temperatures, and allows for parallel DIC measurements. Noncontact strain maps measured with the S4 films and point-wise scanning were directly compared to those from DIC on acrylic, concrete, and aluminum test specimens, including one with subsurface damage. Strain features were more clearly revealed with S4 than with DIC. Finite element method simulations also showed closer agreement with S4 than with DIC results. These findings highlight the potential of S4 strain measurement technology as a promising alternative or complement to existing technologies, especially when accumulated strains must be detected in structures that are not under constant observation.