伝統的な籠の編み目と結晶の模様が一致する新しい物理現象を発見 New physics discovered where crystal patterns match weave of traditional baskets
2022-09-14 ライス大学
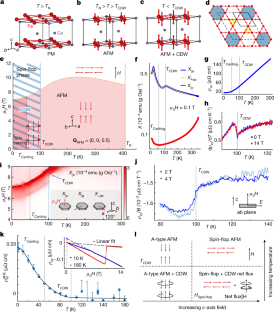
研究者は純粋な鉄ゲルマニウム結晶の研究を行い、結晶を極低温に冷却すると流動電子の定在波が結晶内に自然発生的に現れることを発見した。この電荷密度波は、物質が高温で遷移した磁性状態にあるときに発生した。
カゴメ格子をもつこのような物質で、このことは、磁性に関係している可能性を示唆している。
<関連情報>
- https://news.rice.edu/news/2022/interwoven-charge-and-magnetism-intertwine-kagome-material
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-05034-z
カゴメ格子反強磁性体における電荷密度波の発見 Discovery of charge density wave in a kagome lattice antiferromagnet
Xiaokun Teng,Lebing Chen,Feng Ye,Elliott Rosenberg,Zhaoyu Liu,Jia-Xin Yin,Yu-Xiao Jiang,Ji Seop Oh,M. Zahid Hasan,Kelly J. Neubauer,Bin Gao,Yaofeng Xie,Makoto Hashimoto,Donghui Lu,Chris Jozwiak,Aaron Bostwick,Eli Rotenberg,Robert J. Birgeneau,Jiun-Haw Chu,Ming Yi & Pengcheng Dai
Nature Published:14 September 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05034-z
Abstract
A hallmark of strongly correlated quantum materials is the rich phase diagram resulting from competing and intertwined phases with nearly degenerate ground-state energies1,2. A well-known example is the copper oxides, in which a charge density wave (CDW) is ordered well above and strongly coupled to the magnetic order to form spin-charge-separated stripes that compete with superconductivity1,2. Recently, such rich phase diagrams have also been shown in correlated topological materials. In 2D kagome lattice metals consisting of corner-sharing triangles, the geometry of the lattice can produce flat bands with localized electrons3,4, non-trivial topology5,6,7, chiral magnetic order8,9, superconductivity and CDW order10,11,12,13,14,15. Although CDW has been found in weakly electron-correlated non-magnetic AV3Sb5 (A = K, Rb, Cs)10,11,12,13,14,15, it has not yet been observed in correlated magnetic-ordered kagome lattice metals4,16,17,18,19,20,21. Here we report the discovery of CDW in the antiferromagnetic (AFM) ordered phase of kagome lattice FeGe (refs. 16,17,18,19). The CDW in FeGe occurs at wavevectors identical to that of AV3Sb5 (refs. 10,11,12,13,14,15), enhances the AFM ordered moment and induces an emergent anomalous Hall effect22,23. Our findings suggest that CDW in FeGe arises from the combination of electron-correlations-driven AFM order and van Hove singularities (vHSs)-driven instability possibly associated with a chiral flux phase24,25,26,27,28, in stark contrast to strongly correlated copper oxides1,2 and nickelates29,30,31, in which the CDW precedes or accompanies the magnetic order.