2022-09-06 オークリッジ国立研究所(ORNL)
オークリッジ国立研究所の研究者たちは、電離放射線を用いたがん治療進歩のために、ラジウムの化学的性質を探求した。
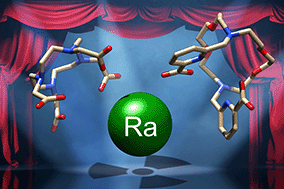
ラジウム223は、骨に転移した癌の治療に用いられる放射性同位元素です。化学的には、ラジウムは体内でカルシウムのように振る舞い、骨に容易に吸着し、がん細胞を破壊し、患者の痛みを軽減する。ラジウム療法は他の癌の治療にも応用できる可能性があるが、ラジウムの化学的性質に関する洞察が必要である。
ORNLのNikki Thiele氏は、「骨ではなく軟組織をターゲットにできるキレーターやキャリア分子を使って、体内でのラジウムの挙動を変えることができますが、ラジウム研究の難しさのために、これらを設計することは困難でした。研究チームはラジウムキレート作用の詳細を原子レベルで捉え、これまで報告された中で最も高い成功率を持つキレート剤を発見しました。」
<関連情報>
- https://www.ornl.gov/news/cancer-fighting-chemistry
- https://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2022/CC/D2CC03156F
標的α療法に向けたラジウムイオンの配位化学の解明 Elucidating the coordination chemistry of the radium ion for targeted alpha therapy
Alexander S. Ivanov, Megan E. Simms, Vyacheslav S. Bryantsev, Paul D. Benny, Justin R. Griswold, Laetitia H. Delmau and Nikki A. Thiele
Chemical Communications Published19 Aug 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CC03156F
Abstract
The coordination chemistry of Ra2+ is poorly defined, hampering efforts to design effective chelators for 223Ra-based targeted alpha therapy. Here, we report the complexation thermodynamics of Ra2+ with the biomedically-relevant chelators DOTA and macropa. Our work reveals the highest affinity chelator to date for Ra2+ and advances our understanding of key factors underlying complex stability and selectivity for this underexplored ion.