バクテリア、菌類、地衣類などの表面層が、大気中に舞い上がる塵の量を低減する A surface layer of bacteria, fungi and lichen amongst others reduces the amount of dust stirred up into the atmosphere
2022-05-17 マックス・プランク研究所
<関連情報>
- https://www.mpg.de/18648634/0517-chem-dust-catcher
- s-biological-crusts-152990-x?c=2249
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41561-022-00942-1
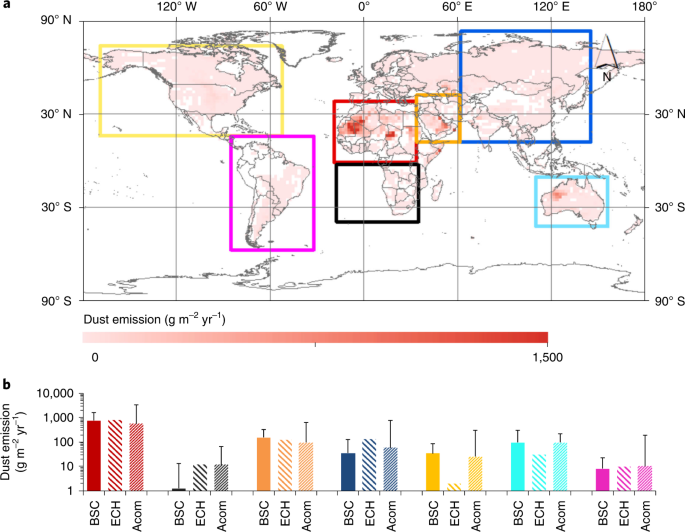
生物学的土壌クラストが制御するエオリアダストの地球循環と気候への影響 Global cycling and climate effects of aeolian dust controlled by biological soil crusts
E. Rodriguez-Caballero,T. Stanelle,S. Egerer,Y. Cheng,H. Su,Y. Canton,J. Belnap,M. O. Andreae,I. Tegen,C. H. Reick,U. Pöschl & B. Weber
Nature Geoscience Published:16 May 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-022-00942-1
Abstract
Biological soil crusts (biocrusts) cover ~12% of the global land surface. They are formed by an intimate association between soil particles, photoautotrophic and heterotrophic organisms, and they effectively stabilize the soil surface of drylands. Quantitative information on the impact of biocrusts on the global cycling and climate effects of aeolian dust, however, is not available. Here, we combine the currently limited experimental data with a global climate model to investigate the effects of biocrusts on regional and global dust cycling under current and future conditions. We estimate that biocrusts reduce the global atmospheric dust emissions by ~60%, preventing the release of ~0.7 Pg dust per year. Until 2070, biocrust coverage is expected to be severely reduced by climate change and land-use intensification. The biocrust loss will cause an increased dust burden, leading to a reduction of the global radiation budget of around 0.12 to 0.22 W m−2, corresponding to about 50% of the total direct forcing of anthropogenic aerosols. This biocrust control on dust cycling and its climate impacts have important implications for human health, biogeochemical cycling and the functioning of the ecosystems, and thus should be considered in the modelling, mitigation and management of global change.