(New Chip for Waking Up Small Wireless Devices Could Extend Battery Life)
2019/11/12 アメリカ合衆国・カ リフォルニア大 学サンディエゴ 校(UCSD)
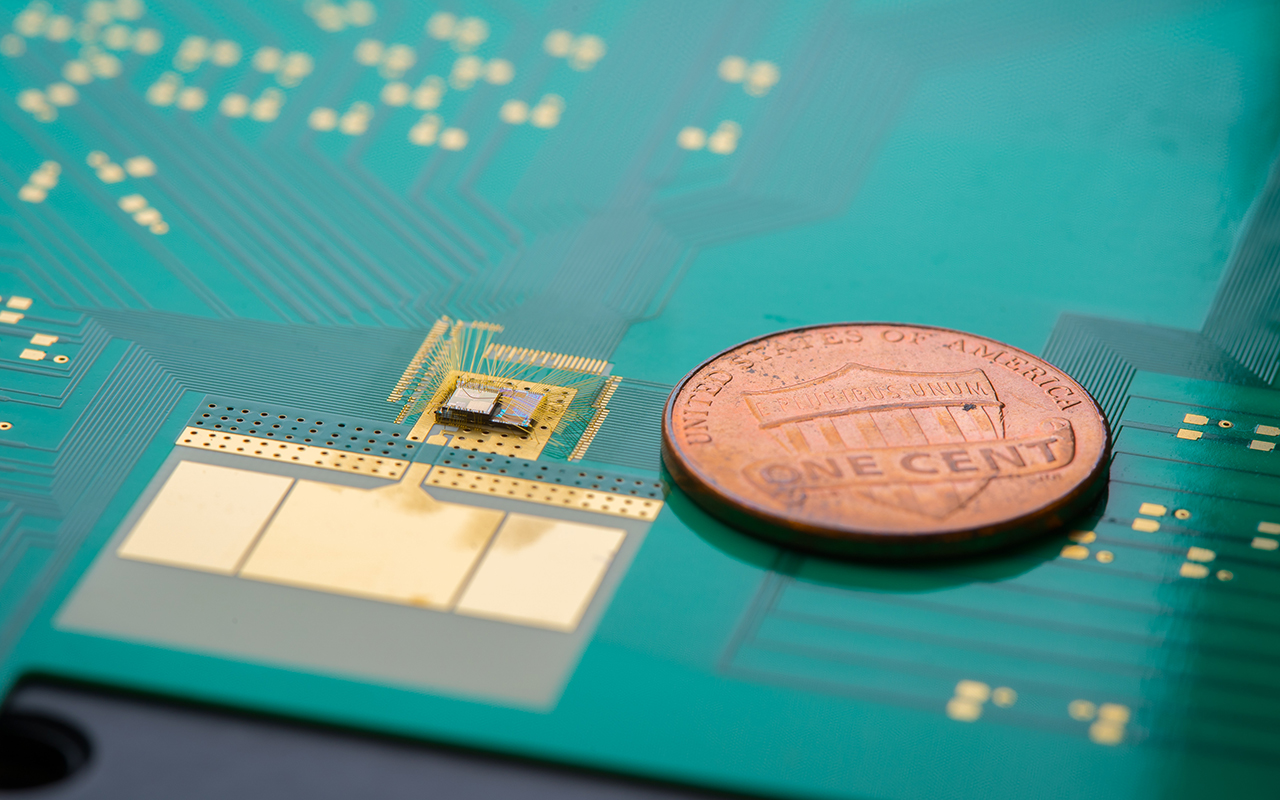
・ UCSD が、IoT デバイスやウェアラブルの電池交換の必要性を大幅に低減・排除させる、省エネチッ プを開発。
・ いわゆるウェイクアップ・レシーバである同チップは、通信等の作動時以外ではデバイスを休止状態 に留めて消費電力を低減する。
・ デバイスはネットワークと同期する正確なタイミングを認識できないため、通信相手の無い場合でも 周期的に起動して電力を浪費。ウェイクアップ・レシーバを取り入れれば、小型 IoT デバイスの電池寿 命を数か月~数年延長できる。
・ 同チップは、ウェイクアップ・シグネチャと呼ばれる特定の無線信号を常時チェックしてメインデバイ スを起動させる。これらの作業に要する電力は、22.3nW と極僅か(LED 夜間照明の消費電力の約 1/50 万)。
・ 同チップ設計の主要な特徴は、他のウェイクアップ・レシーバよりも高い、衛星通信や速度検出用の 9GHz周波数帯の無線信号を使用すること。高周波数利用により、アンテナ、変圧器や外部コンポー ネント等全てが微細化され、ナノワットスケールの 1/20 という大幅に小型のパッケージに納まる。
・ さらに、屋外の-10℃(14℉)から 40℃(104℉)までの幅広い温度領域にて安定して作動。これは他の ナノワットレシーバでは不可能。通常、数度の温度変化でも低電力ウェイクアップ・レシーバの性能は 低下する。
・ 同チップによるレシーバのナノワットレベルの消費電力、小型パッケージサイズ(4.55 ㎠)、高感度(- 69.5dBm)および温度性能は、これまでに報告されたものの中で最も優れていると考える。 ・ 同レシーバがウェイクアップ・シグネチャを検出してからデバイスを起動させるのに 540 ミリ秒かかる という、レイテンシ―(通信遅延)の課題があるが、対象となるアプリケーションではこの程度の遅れは 問題にならないと考える。
・ 本研究は、米国防高等研究計画局(DARPA)による支援と国海軍研究局(ONR)の DURIP アワードを 通じて購入した機器で実施した。
URL: https://ucsdnews.ucsd.edu/pressrelease/new-chip-for-waking-up-small-wireless-devicescould-extend-battery-life
(関連情報)
IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 掲載論文(アブストラクトのみ:全文は有料)
A 22.3-nW, 4.55 cm² Temperature-Robust Wake-Up Receiver Achieving a Sensitivity of -69.5 dBm at 9 GHz
URL: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8890666
<NEDO海外技術情報より>



