ニューラル・フィールド・ネットワークは、他のサンプルで学習させる必要がない Neural field network doesn’t need to be trained on other samples
2022-09-19 ワシントン大学セントルイス
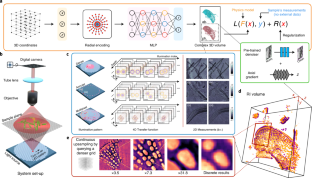
この研究の鍵は、空間座標から対応する物理量へのマッピングを学習する特殊な機械学習システムである、ニューラルフィールドネットワークを使用することであった。
ネットワークの学習に使用する画像は、他の顕微鏡画像と同じで、細胞を下から照らし、その中を光が通り抜け、反対側で捉えられることで画像が生成される。
細胞の外観をいくつか持っているので、それらの画像を使ってモデルを訓練することができる。この訓練は、細胞の内部構造の一部を捉えた画像から、サンプル内のある位置に関する情報をモデルに与えることで行われる。
すると、ネットワークはその構造を再現するために最善の努力をする。出力が正しければ、その経路が強化される。予測値が実際の測定値と一致すれば、ネットワークは、元の2次元画像では捉えられなかった細胞の部分を埋める準備が整う。
このとき、モデルには細胞の完全な連続表現の情報が含まれている。ニューロフィールドネットワークによっていつでも再作成できるので、データの多い画像ファイルを保存する必要はない。
どんな座標でも入れて、そのビューを生成することができる。異なる角度から全く新しいビューを生成することもできる。
<関連情報>
- https://source.wustl.edu/2022/09/machine-learning-generates-3d-model-from-2d-pictures/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-022-00530-3
ニューロフィールドを用いた離散的な強度のみの測定値からの連続的な3次元屈折率マップの復元 Recovery of continuous 3D refractive index maps from discrete intensity-only measurements using neural fields
Renhao Liu,Yu Sun,Jiabei Zhu,Lei Tian & Ulugbek S. Kamilov
Nature Machine Intelligence Published:16 September 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-022-00530-3
Abstract
Intensity diffraction tomography (IDT) refers to a class of optical microscopy techniques for imaging the three-dimensional refractive index (RI) distribution of a sample from a set of two-dimensional intensity-only measurements. The reconstruction of artefact-free RI maps is a fundamental challenge in IDT due to the loss of phase information and the missing-cone problem. Neural fields has recently emerged as a new deep learning approach for learning continuous representations of physical fields. The technique uses a coordinate-based neural network to represent the field by mapping the spatial coordinates to the corresponding physical quantities, in our case the complex-valued refractive index values. We present Deep Continuous Artefact-free RI Field (DeCAF) as a neural-fields-based IDT method that can learn a high-quality continuous representation of a RI volume from its intensity-only and limited-angle measurements. The representation in DeCAF is learned directly from the measurements of the test sample by using the IDT forward model without any ground-truth RI maps. We qualitatively and quantitatively evaluate DeCAF on the simulated and experimental biological samples. Our results show that DeCAF can generate high-contrast and artefact-free RI maps and lead to an up to 2.1-fold reduction in the mean squared error over existing methods.