2022-06-22 ノースカロライナ州立大学(NCState)
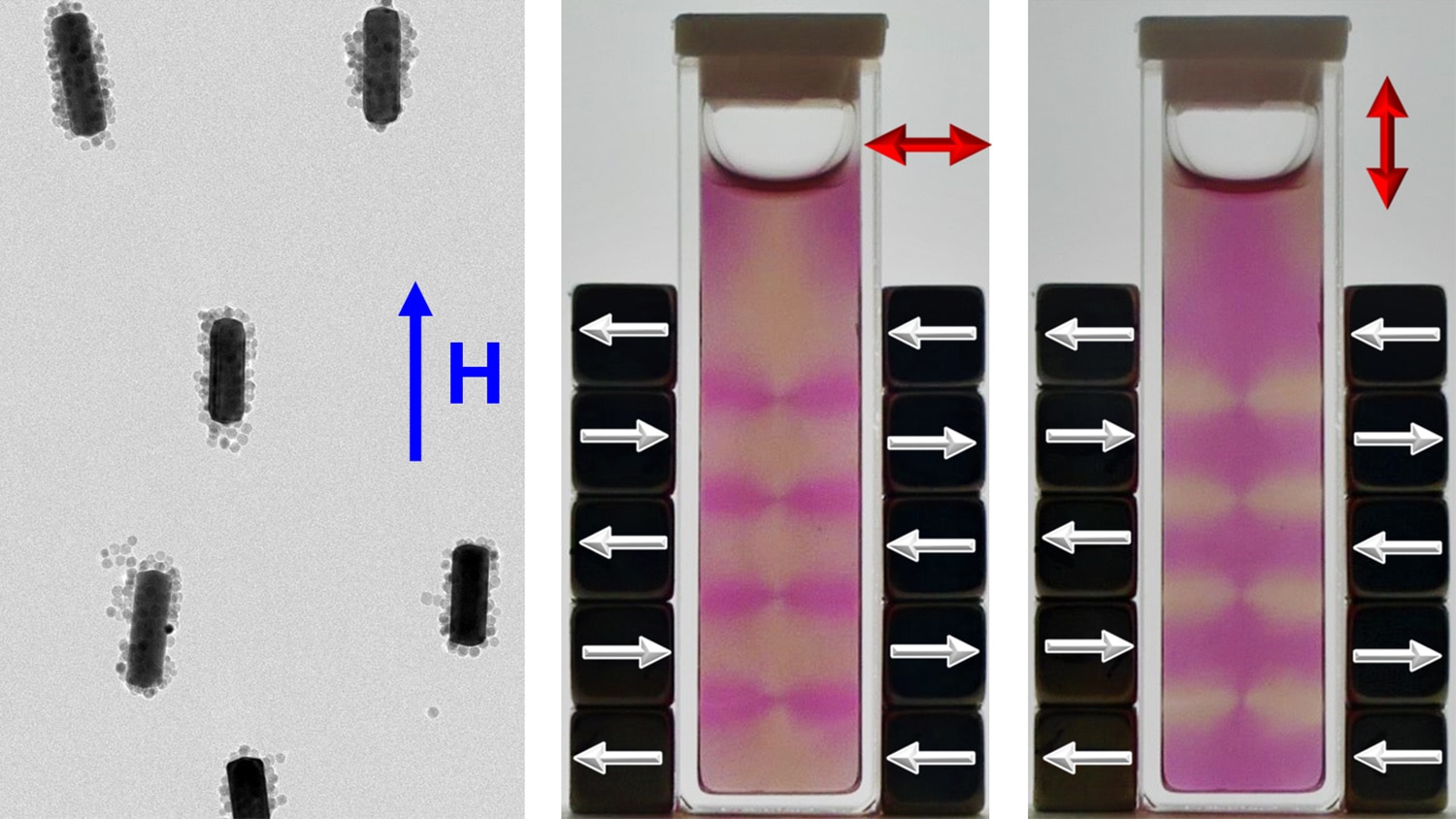
Electron micrograph of gold nanorods overcoated with iron oxide nanoparticles and aligned in a magnetic field. Image Credit: Mehedi H. Rizvi
金ナノロッドの寸法を工夫することで、吸収・散乱される光の波長を調整することができます。また、金ナノロッドの配向を磁気的に制御することで、どの波長に反応するかをさらに制御・調節することも可能です。
磁場を用いてアライメントを制御することは、実際にナノロッドに触れることなく、アライメントを制御できることを意味します。
研究者達は、金ナノロッドと酸化鉄ナノ粒子の別々の溶液を合成しています。この溶液を混ぜると、酸化鉄ナノ粒子が金ナノロッドの表面に集合する。こうしてできた「コーティング」されたナノロッドは、低強度の磁場を用いて制御することができる。
<関連情報>
- https://news.ncsu.edu/2022/06/technique-allows-researchers-to-align-gold-nanorods-with-magnetic-fields/
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202203366
酸化鉄ナノ粒子で被覆された金ナノロッドのプラズモン制御のための磁気整列法 Magnetic Alignment for Plasmonic Control of Gold Nanorods Coated with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
Mehedi H. Rizvi,Ruosong Wang,Jonas Schubert,William D. Crumpler,Christian Rossner,Amy L. Oldenburg,Andreas Fery,Joseph B. Tracy
Advanced Materials Published:09 June 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202203366
Abstract
Plasmonic nanoparticles that can be manipulated with magnetic fields are of interest for advanced optical applications, diagnostics, imaging, and therapy. Alignment of gold nanorods yields strong polarization-dependent extinction, and use of magnetic fields is appealing because they act through space and can be quickly switched. In this work, cationic polyethyleneimine-functionalized superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles (NPs) are deposited on the surface of anionic gold nanorods coated with bovine serum albumin. The magnetic gold nanorods (MagGNRs) obtained through mixing maintain the distinct optical properties of plasmonic gold nanorods that are minimally perturbed by the magnetic overcoating. Magnetic alignment of MagGNRs arising from magnetic dipolar interactions on the anisotropic gold nanorod core is comprehensively characterized, including structural characterization and enhancement (suppression) of the longitudinal surface plasmon resonance and suppression (enhancement) of the transverse surface plasmon resonance for light polarized parallel (orthogonal) to the magnetic field. MagGNRs can also be driven in rotating magnetic fields to rotate at frequencies of at least 17 Hz. For suitably large gold nanorods (148 nm long) and Fe3O4 NPs (13.4 nm diameter), significant alignment is possible even in modest (<500 Oe) magnetic fields. An analytical model provides a unified understanding of the magnetic alignment of MagGNRs.
This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved