赤外線の放射が、光学波長での観測では見えない秘密を解き明かす Infrared emissions reveal secrets invisible with optical wavelength observations
2022-06-01 カリフォルニア大学校アーバイン校(UCI)
・カリフォルニア大学アーバイン校、オックスフォード大学、その他の機関の天文学者からなる国際チームは、銀河間物質中の気相金属の存在比を調べるために、酸素と窒素の比率のデータを、ハーシェル宇宙望遠鏡のデータと、NASAのSOFIA空中天文台(成層圏赤外線天文台)で観測することにした。
・複数年にわたる観測で得られた赤外線データを分析することにより、以前の研究では欠けているとされていた、より重い元素が局所銀河に存在する証拠を発見しました。
・ネイチャー・アストロノミー誌に掲載された論文では、可視光線では薄暗いが赤外線では太陽の何兆倍もの明るさを持つ5つの銀河を調査しています。これらの銀河と近隣の星系との相互作用により、ガスが移動し、崩壊することで、驚異的な星形成の条件が整うのです。
<関連情報>
- https://news.uci.edu/2022/06/01/uci-led-astronomy-team-finds-evidence-of-galactic-metal-shrouded-in-dust/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41550-022-01679-y
超大質量赤外線銀河の低い気相メタリック度は、塵によるオブスキュアの結果である Low gas-phase metallicities of ultraluminous infrared galaxies are a result of dust obscuration
Nima Chartab,Asantha Cooray,Jingzhe Ma,Hooshang Nayyeri,Preston Zilliot,Jonathan Lopez,Dario Fadda,Rodrigo Herrera-Camus,Matthew Malkan,Dimitra Rigopoulou,Kartik Sheth & Julie Wardlow
Nature Astronomy Published:26 May 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-022-01679-y
Abstract
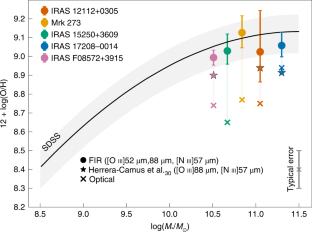
Optical spectroscopic measurements show that gas in dusty, starbursting galaxies known as ultraluminous infrared galaxies (ULIRGs) in the local Universe has a significantly lower metal content than that of gas in star-forming galaxies with similar masses. This low metal content has resulted in the claim that ULIRGs are primarily fuelled by metal-poor gas falling into those galaxy merger systems from large distances. Here we report a new set of gas-phase metal abundance measurements taken in local ULIRGs using emission lines at far-infrared wavelengths tracing oxygen and nitrogen. These new data show that ULIRGs lie on the fundamental metallicity relation determined by the stellar mass, metal abundance and star formation rate as the key observational parameters. Instead of metal-poor gas accretion, the new data suggest that the underabundance of metals derived from optical emission lines is probably due to heavy dust obscuration associated with the starburst. As dust-obscured, infrared-bright galaxies dominate the star formation rate density of the Universe during the peak epoch of star formation, we caution the use of rest-frame optical measurements alone to study the metal abundances of galaxies at redshifts of 2–3.