2022-11-29 ノースカロライナ州立大学(NCState)
フルラナーとイベルメクチンは、犬や猫などのペットのノミやダニを殺すために使用されますが、トコジラミを殺す効果も検証されました。NC州立大学獣医学部の昆虫学者と獣医学者が共同で、実験台で薬剤を混ぜた血液を害虫が摂取した後と、薬剤を摂取または局所投与したニワトリをトコジラミが咬んで食べた後、異なる実験でトコジラミの死亡率をテストしました。
フルララナーは、比較的新しく、効き目が長く、主にコンパニオンアニマルに使用される抗寄生虫薬ですが、ヨーロッパとオーストラリアでは養鶏業への使用が承認されています。イベルメクチンは、ペット用のほか、アフリカを中心とした人間や大型動物にも有効な寄生虫駆除薬です。
両薬剤は実験室で強力な効果を示し、ほとんどのトコジラミを殺しましたが、一般的な殺虫剤に抵抗性を示すトコジラミに対しては、フルラナーの方がはるかに効果的な効果を示しました。と、NC StateのBlanton J. Whitmire Distinguished Professor of EntomologyのCoby Schal氏は述べた。この研究を説明する論文の筆頭著者であるフルラレンは、「この薬剤は昆虫の神経系にある受容体に作用する。この薬剤を投与したニワトリを餌とするトコジラミを殺すのに非常に効果的でした。一方、イベルメクチンは投与されたニワトリを餌とするトコジラミには効果がありませんでした。」
研究者らは、家禽の飲料水にフルラネールを投与することがトコジラミ対策として有効であると述べている。また、モニタリング、教育、加熱処理、フララナーなどの組み合わせが、トコジラミが蔓延した養鶏場からトコジラミを根絶する鍵を握っている可能性があるとも述べている。
<関連情報>
- https://news.ncsu.edu/2022/11/common-veterinary-drugs-effective-against-bed-bugs/
- https://parasitesandvectors.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13071-022-05555-6
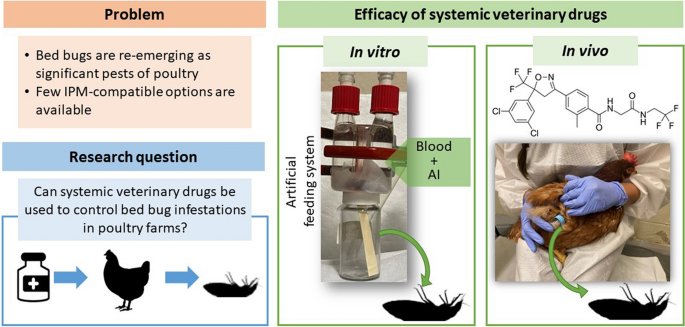
養鶏場におけるトコジラミ(Cimex lectularius)防除のための動物用全身投与薬。Systemic veterinary drugs for control of the common bed bug, Cimex lectularius, in poultry farms
Maria A. González-Morales, Andrea E. Thomson, Olivia A. Petritz, Rocio Crespo, Ahmed Haija, Richard G. Santangelo & Coby Schal
Parasites & Vectors volume 15, Article number: 431 (2022)
Abstract
Background
The common bed bug, Cimex lectularius L., is a hematophagous ectoparasite that was a common pest in poultry farms through the 1960s. Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) and organophosphates eradicated most infestations, but concurrent with their global resurgence as human ectoparasites, infestations of bed bugs have been reappearing in poultry farms. Although the impact of bed bugs on chicken health has not been quantified, frequent biting and blood-feeding are expected to cause stress, infections and even anemia in birds. Bed bug control options are limited due to the sensitive nature of the poultry environment, limited products labeled for bed bug control and resistance of bed bug populations to a broad spectrum of active ingredients. Veterinary drugs are commonly used to control endo- and ectoparasites in animals. In this study, we evaluated the effects of two common veterinary drugs on bed bugs by treating the host with systemic antiparasitic drugs.
Methods
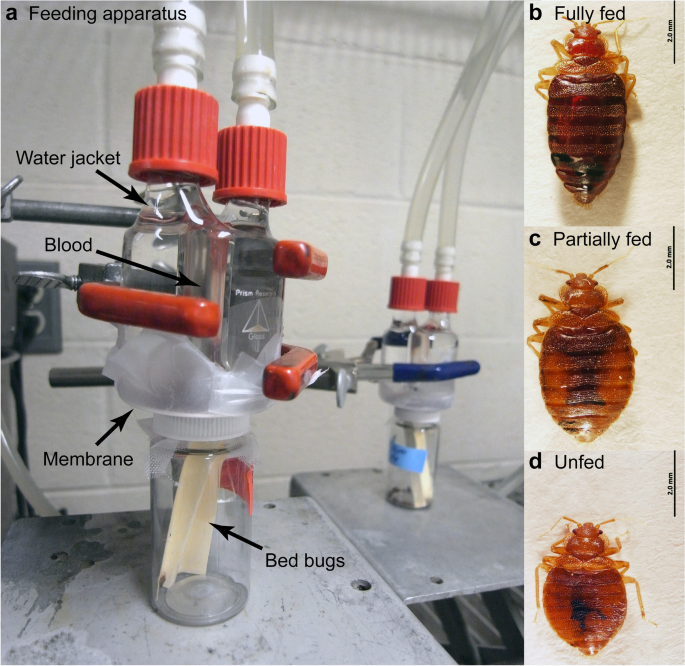
We conducted dose–response studies of ivermectin and fluralaner against several bed bug strains using a membrane feeding system. Also, different doses of these drugs were given to chickens and two delivery methods (topical treatment and ingestion) were used to evaluate the efficacy of ivermectin and fluralaner on bed bug mortality.
Results
Using an artificial feeding system, both ivermectin and fluralaner caused high mortality in insecticide-susceptible bed bugs, and fluralaner was found to be effective on pyrethroid- and fipronil-resistant bed bugs. Ivermectin was ineffective in chickens either by the topical treatment or ingestion, whereas bed bugs that fed on chickens which had ingested fluralaner suffered high mortality when feeding on these chickens for up to 28 days post treatment.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that systemic ectoparasitic drugs have great potential for practical use to control bed bug infestations in poultry farms. These findings also demonstrate the efficacy of fluralaner (and potentially other isoxazolines) as a potent new active ingredient for bed bug control.
Graphical Abstract