科学者たちが、100年前の材料を次世代メモリやロジックデバイスのための薄膜に変身させた Scientists turn century-old material into a thin film for next-gen memory and logic devices
2022-06-22 ローレンスバークレー国立研究所(LBNL)
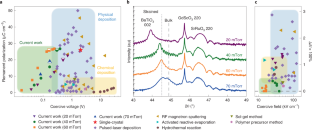
チタン酸バリウムの結晶は、小さな電界に素早く反応し、電界を取り除いた後も、物質を構成する帯電した原子の向きを可逆的かつ永久的に反転させることができる。これは、論理装置や記憶装置において、「0」と「1」の状態を切り替える方法であるが、そのためには1,000ミリボルト(mV)以上の電圧が必要である。
人間の髪の毛の1000分の1にも満たないわずか25ナノメートルのBaTiO3薄膜を作成する方法を開発しました。
<関連情報>
- https://newscenter.lbl.gov/2022/06/22/new-ultrathin-capacitor-could-enable-energy-efficient-microchips/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41563-022-01266-6
BaTiO3における超低電圧スイッチングの実現 Enabling ultra-low-voltage switching in BaTiO3
Y. Jiang,E. Parsonnet,A. Qualls,W. Zhao,S. Susarla,D. Pesquera,A. Dasgupta,M. Acharya,H. Zhang,T. Gosavi,C.-C. Lin,D. E. Nikonov,H. Li,I. A. Young,R. Ramesh & L. W. Martin
Nature Materials
Abstract
Single crystals of BaTiO3 exhibit small switching fields and energies, but thin-film performance is considerably worse, thus precluding their use in next-generation devices. Here, we demonstrate high-quality BaTiO3 thin films with nearly bulk-like properties. Thickness scaling provides access to the coercive voltages (<100 mV) and fields (<10 kV cm−1) required for future applications and results in a switching energy of <2 J cm−3 (corresponding to <2 aJ per bit in a 10 × 10 × 10 nm3 device). While reduction in film thickness reduces coercive voltage, it does so at the expense of remanent polarization. Depolarization fields impact polar state stability in thicker films but fortunately suppress the coercive field, thus driving a deviation from Janovec–Kay–Dunn scaling and enabling a constant coercive field for films <150 nm in thickness. Switching studies reveal fast speeds (switching times of ~2 ns for 25-nm-thick films with 5-µm-diameter capacitors) and a pathway to subnanosecond switching. Finally, integration of BaTiO3 thin films onto silicon substrates is shown. We also discuss what remains to be demonstrated to enable the use of these materials for next-generation devices.