研究チームは、ディープマシンラーニングによって強化された超高解像度顕微鏡を使用しました。 Team used super high-resolution microscopy enhanced by deep machine learning
2023-01-26 カリフォルニア大学校アーバイン校(UCI)
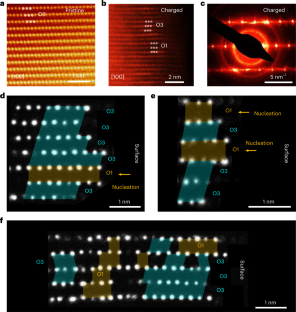
◆このたび、カリフォルニア大学アーバイン校とブルックヘブン国立研究所の研究者らは、『Nature Materials』に掲載された論文で、次世代電池の有望な構成要素と考えられている高ニッケル含有層状正極の詳細な調査を行いました。カリフォルニア大学率いるチームは、超解像電子顕微鏡と機械学習を組み合わせることで、リチウムイオン電池で挟まれた材料の界面における微細な変化を読み解くことができました。
<関連情報>
- https://news.uci.edu/2023/01/26/uci-researchers-decipher-atomic-scale-imperfections-in-lithium-ion-batteries/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41563-022-01461-5
リチウムイオン電池用高Ni含有層状正極材料における複雑な層内遷移モチーフの解明に成功 Resolving complex intralayer transition motifs in high-Ni-content layered cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries
Chunyang Wang,Xuelong Wang,Rui Zhang,Tianjiao Lei,Kim Kisslinger & Huolin L. Xin
Nature Materials Published:26 January 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-022-01461-5
Abstract
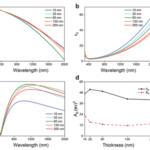
High-Ni-content layered materials are promising cathodes for next-generation lithium-ion batteries. However, investigating the atomic configurations of the delithiation-induced complex phase boundaries and their transitions remains challenging. Here, by using deep-learning-aided super-resolution electron microscopy, we resolve the intralayer transition motifs at complex phase boundaries in high-Ni cathodes. We reveal that an O3 → O1 transformation driven by delithiation leads to the formation of two types of O1–O3 interface, the continuous- and abrupt-transition interfaces. The interfacial misfit is accommodated by a continuous shear-transition zone and an abrupt structural unit, respectively. Atomic-scale simulations show that uneven in-plane Li+ distribution contributes to the formation of both types of interface, and the abrupt transition is energetically more favourable in a delithiated state where O1 is dominant, or when there is an uneven in-plane Li+ distribution in a delithiated O3 lattice. Moreover, a twin-like motif that introduces structural units analogous to the abrupt-type O1–O3 interface is also uncovered. The structural transition motifs resolved in this study provide further understanding of shear-induced phase transformations and phase boundaries in high-Ni layered cathodes.