2024-02-21 ミネソタ大学
<関連情報>
- https://cse.umn.edu/college/news/new-study-first-step-predicting-carbon-emissions-agriculture
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-43860-5
知識誘導型機械学習により、農業生態系における炭素循環定量化を改善できる Knowledge-guided machine learning can improve carbon cycle quantification in agroecosystems
Licheng Liu,Wang Zhou,Kaiyu Guan,Bin Peng,Shaoming Xu,Jinyun Tang,Qing Zhu,Jessica Till,Xiaowei Jia,Chongya Jiang,Sheng Wang,Ziqi Qin,Hui Kong,Robert Grant,Symon Mezbahuddin,Vipin Kumar & Zhenong Jin
Nature Communications Published:08 January 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-43860-5
Abstract
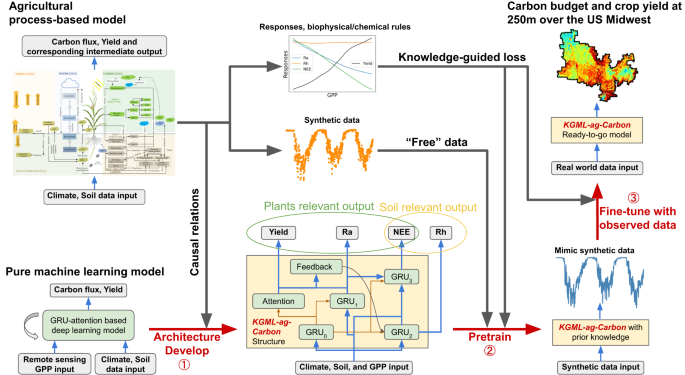
Accurate and cost-effective quantification of the carbon cycle for agroecosystems at decision-relevant scales is critical to mitigating climate change and ensuring sustainable food production. However, conventional process-based or data-driven modeling approaches alone have large prediction uncertainties due to the complex biogeochemical processes to model and the lack of observations to constrain many key state and flux variables. Here we propose a Knowledge-Guided Machine Learning (KGML) framework that addresses the above challenges by integrating knowledge embedded in a process-based model, high-resolution remote sensing observations, and machine learning (ML) techniques. Using the U.S. Corn Belt as a testbed, we demonstrate that KGML can outperform conventional process-based and black-box ML models in quantifying carbon cycle dynamics. Our high-resolution approach quantitatively reveals 86% more spatial detail of soil organic carbon changes than conventional coarse-resolution approaches. Moreover, we outline a protocol for improving KGML via various paths, which can be generalized to develop hybrid models to better predict complex earth system dynamics.