2023-10-30 NASA
◆Junoは、赤外線分光計JIRAMを使用し、前例のない空間分解能でデータを収集しました。これらの観測は、ガニメデの内部海からの成分が表面に達した可能性を示唆しており、これにより宇宙の謎が一歩解明されました。同様に、他の木星の衛星に対するJunoのフライバイも行われており、これにより太陽系の未知の領域に関する情報が得られています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.nasa.gov/missions/juno/salts-and-organics-observed-on-ganymedes-surface-by-nasas-juno/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41550-023-02107-5
ジュノー搭載のJIRAM分光計が観測したガニメデ表面の塩類と有機物 Salts and organics on Ganymede’s surface observed by the JIRAM spectrometer onboard Juno
Federico Tosi,Alessandro Mura,Alessandra Cofano,Francesca Zambon,Christopher R. Glein,Mauro Ciarniello,Jonathan I. Lunine,Giuseppe Piccioni,Christina Plainaki,Roberto Sordini,Alberto Adriani,Scott J. Bolton,Candice J. Hansen,Tom A. Nordheim,Alessandro Moirano,Livio Agostini,Francesca Altieri,Shawn M. Brooks,Andrea Cicchetti,Bianca Maria Dinelli,Davide Grassi,Alessandra Migliorini,Maria Luisa Moriconi,Raffaella Noschese,Pietro Scarica,Giuseppe Sindoni,Stefania Stefani & Diego Turrini
Nature Astronomy Published:30 October 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-023-02107-5
Abstract
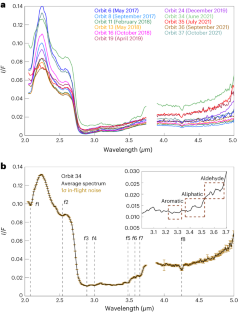
The surface of Ganymede exhibits diversity in composition, interpreted as indicative of geological age differences between dark and bright terrains. Observations from Galileo and Earth-based telescopes have revealed the presence of both water ice and non-ice material, indicative of either endogenic or exogenic processes, or some combination. However, these observations attained a spatial resolution that was too coarse to reveal the surface composition at a local scale. Here we present the high-spatial-resolution infrared spectra of Ganymede observed with the Jovian InfraRed Auroral Mapper onboard the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s Juno spacecraft during a close flyby that occurred on 7 June 2021. We found that at a pixel resolution <1 km, the surface of Ganymede exhibits signatures diagnostic of hydrated sodium chloride, ammonium chloride and sodium/ammonium carbonate, as well as organic compounds, possibly including aliphatic aldehydes. Carbon dioxide shows up mostly at trailing longitudes. The composition and spatial distribution of these salts and organics suggest that their origin is endogenic, resulting from the extrusion of subsurface brines, whose chemistry reflects the water–rock interaction inside Ganymede.