2023-01-24 オークリッジ国立研究所(ORNL)
◆希土類元素はモナザイトのような鉱石の中に自然に一緒に含まれていますが、回収するのは経済的に困難です。貴重な鉱石と不要な物質を分離するための新しいアプローチが必要なのです。
◆研究チームは、理論と実験を組み合わせてモナザイトの原子レベルの特性を明らかにし、浮遊回収分子(混合鉱物スラリーから気泡に乗ったモナザイト粒子を浮き上がらせるライフジャケットのような働きをする物質)の設計に重要な表面特性を初めて明らかにした。
◆「私たちの研究は、処理中に高品位の鉱石と低品質の物質を分離するために用いられる泡沫浮選技術に必要な材料を扱っています。基礎研究は、モナザイトの回収をより効率的かつ費用対効果の高いものにするために、将来の回収装置を調整するのに役立ちます」とORNLのVyacheslav Bryantsevは述べています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.ornl.gov/news/designer-molecules-may-help-valuable-minerals-float
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jpcc.2c06308
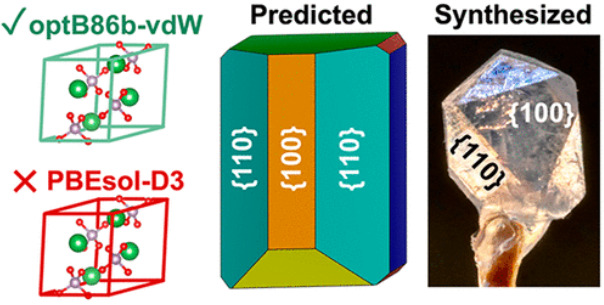
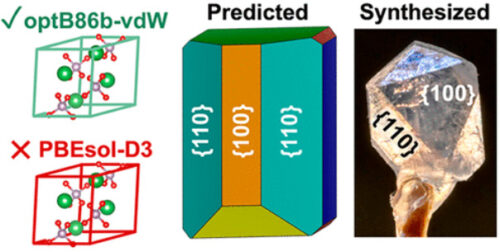
密度汎関数理論と実験によるランタンモナザイトの表面化学と結晶形状の特性評価 Characterization of Lanthanum Monazite Surface Chemistry and Crystal Morphology through Density Functional Theory and Experimental Approaches
Luke D. Gibson, K. Jayanthi, Shuhao Yang, Nikki Thiele, Lawrence M. Anovitz, Robert L. Sacci, Alexandra Navrotsky and Vyacheslav S. Bryantsev
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C Published:October 28, 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.2c06308
Abstract
Monazite is a rare earth element (REE)-containing mineral that consists of (REE)PO4 formal units and is one of the most important sources of these critical materials. The concentration of REEs from mined monazite ore often involves froth flotation, which is a beneficiation process that enhances the efficiency of downstream processing. The effectiveness of froth flotation is largely governed by the ability of collector agents to selectively bind to monazite particles. Thus, a molecular-level understanding of monazite interfacial chemistry is integral to the design of effective collector agents. To address this need, we performed density functional theory (DFT) calculations and a variety of experimental techniques to characterize La-monazite and elucidate its crystal morphology. Interestingly, we find minimal differences in the predicted morphologies of La-monazite for hydrous and anhydrous environments, which are largely dominated by low-index facets (e.g., {110}, {100}, and {010}). Indexing of synthesized La-monazite crystals via X-ray diffraction also uncovers {110} and {100} as the predominant facets. The average surface energies of 0% and 100% water coverage La-monazite crystals were predicted to be 0.87 and 0.76 J/m2, respectively, while calorimetry suggests values of 1.30 and 1.15 J/m2, respectively. The apparent discrepancies between the theoretical and experimental values are expected and attributed to defects present in physical crystals, in contrast to the perfect mineral surfaces in simulations. The difference in surface energy between the 0% and 100% water coverage morphologies predicted by theory is consistent with the value measured via calorimetry. DFT reveals a wide range of adsorption energies for water across the studied facets, but in all cases, water is predicted to strongly bind to monazite surfaces with an average adsorption energy of −92.7 kJ/mol for a La-monazite single crystal. This study provides the groundwork necessary for the rational design of froth flotation collector agents by granting molecular-level insight into the predominant facets of monazite.