2022-11-08 オーストラリア連邦研究会議(ARC)
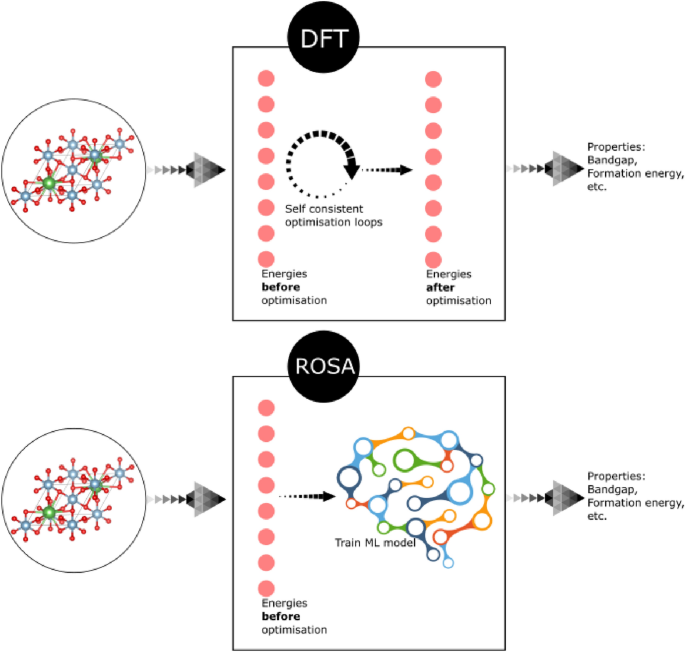
これまで、材料がどのように振る舞うかを示す重要なデータを得るには、密度汎関数理論(DFT)のような複雑な計算が必要でしたが、スーパーコンピュータを使用すると数時間から数日かかることがある。
機械学習モデルは、スーパーコンピューティングに代わる、より迅速で安価な手段を提供する。完全なDFT計算の中の不完全な部分を使用することで、同じ正確な結果を迅速に生成するように学習させることができ、その過程で時間、費用、エネルギーを節約することができる。
現在、材料に関する大規模な生データが機械学習モデルによる分析に利用できるようになっているが、まず、材料の構造とその他の関連する特性とを対応付けることができる属性または「記述子」のグループを選択する必要がある。
研究者たちは、物質のエネルギー的性質を利用して生成したROSA(robust one-shot ab initio)記述子を用いて、機械学習モデルを訓練し、素晴らしい結果を得ました。
開発したこの記述子は、結晶、有機金属骨格、分子の特性について正確な予測結果を出している。
ROSA記述子は、バンドギャップや形成エネルギー、材料の機械的特性や振動特性、さらには分子特性など、数多くの有用なデータを高い精度で予測することができた。
<関連情報>
- https://excitonscience.com/news/materials-science-unleashed-rosa-renders-supercomputers-redundant
- https://jcheminf.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13321-022-00658-9
自然に意味のある効率的な記述子:ロバストな第一原理記述子に基づく材料特性の機械学習 Naturally-meaningful and efficient descriptors: machine learning of material properties based on robust one-shot ab initio descriptors
Sherif Abdulkader Tawfik &Salvy P. Russo
Journal of Cheminformatics Published:08 November 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1186/s13321-022-00658-9
Abstract
Establishing a data-driven pipeline for the discovery of novel materials requires the engineering of material features that can be feasibly calculated and can be applied to predict a material’s target properties. Here we propose a new class of descriptors for describing crystal structures, which we term Robust One-Shot Ab initio (ROSA) descriptors. ROSA is computationally cheap and is shown to accurately predict a range of material properties. These simple and intuitive class of descriptors are generated from the energetics of a material at a low level of theory using an incomplete ab initio calculation. We demonstrate how the incorporation of ROSA descriptors in ML-based property prediction leads to accurate predictions over a wide range of crystals, amorphized crystals, metal–organic frameworks and molecules. We believe that the low computational cost and ease of use of these descriptors will significantly improve ML-based predictions.



