火星着陸船の地震計は、過去2年間に4回の衝突による振動と音を拾いました。この進展は、ブラウン大学の惑星科学者イングリッド・ドーバルの共著で詳述されています。 The Mars lander’s seismometer picked up vibrations and sounds from four impacts in the past two years, a development detailed in a study co-authored by Brown planetary scientist Ingrid Daubar.
2022-09-19 ブラウン大学
確認された4つのメテオロイド(地上に衝突する前の宇宙岩石を指す)のうち、チームが見つけた最初のものは、2021年9月5日に火星の大気圏に突入し、少なくとも3つの破片に爆発し、それぞれクレーターを残した。
それ以前のデータを調べた結果、2020年5月27日、2021年2月18日、2021年8月31日の3つの衝突が確認されました。
火星地震の多くは、地下の岩石が熱と圧力で割れることで発生する。その結果生じる地震波が、異なる物質中を移動することによってどのように変化するかを研究することは、火星の地殻、マントル、コアを研究する方法を提供するものである。
科学者は、その衝突クレーターを数えることによって、惑星表面の年齢を概算することができる。火星では、地球のように地殻変動や活発な火山活動がないため、地表に様々な大きさの衝突クレーターが蓄積されるのに時間がかかっている。現在起きている衝突の頻度に基づいて統計モデルを校正することで、科学者は太陽系の歴史の早い時期にどれくらいの衝突が起きたかを推定することができる。
<関連情報>
- https://www.brown.edu/news/2022-09-19/meteoroid-impacts
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41561-022-01014-0
InSightの地震波・音響波データを用いて火星に新たに形成されたクレーターを特定 Newly formed craters on Mars located using seismic and acoustic wave data from InSight
Raphael F. Garcia,Ingrid J. Daubar,Éric Beucler,Liliya V. Posiolova,Gareth S. Collins,Philippe Lognonné,Lucie Rolland,Zongbo Xu,Natalia Wójcicka,Aymeric Spiga,Benjamin Fernando,Gunnar Speth,Léo Martire,Andrea Rajšić,Katarina Miljković,Eleanor K. Sansom,Constantinos Charalambous,Savas Ceylan,Sabrina Menina,Ludovic Margerin,Rémi Lapeyre,Tanja Neidhart,Nicholas A. Teanby,Nicholas C. Schmerr,Mickaël Bonnin,Marouchka Froment,John F. Clinton,Ozgur Karatekin,Simon C. Stähler,Nikolaj L. Dahmen,Cecilia Durán,Anna Horleston,Taichi Kawamura,Matthieu Plasman,Géraldine Zenhäusern,Domenico Giardini,Mark Panning,Mike Malin & William Bruce Banerdt
Nature Geoscience Published:19 September 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-022-01014-0
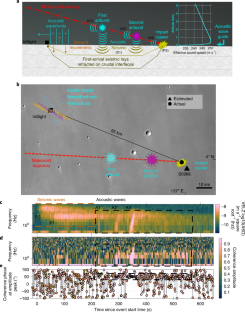
Abstract
Meteoroid impacts shape planetary surfaces by forming new craters and alter atmospheric composition. During atmospheric entry and impact on the ground, meteoroids excite transient acoustic and seismic waves. However, new crater formation and the associated impact-induced mechanical waves have yet to be observed jointly beyond Earth. Here we report observations of seismic and acoustic waves from the NASA InSight lander’s seismometer that we link to four meteoroid impact events on Mars observed in spacecraft imagery. We analysed arrival times and polarization of seismic and acoustic waves to estimate impact locations, which were subsequently confirmed by orbital imaging of the associated craters. Crater dimensions and estimates of meteoroid trajectories are consistent with waveform modelling of the recorded seismograms. With identified seismic sources, the seismic waves can be used to constrain the structure of the Martian interior, corroborating previous crustal structure models, and constrain scaling relationships between the distance and amplitude of impact-generated seismic waves on Mars, supporting a link between the seismic moment of impacts and the vertical impactor momentum. Our findings demonstrate the capability of planetary seismology to identify impact-generated seismic sources and constrain both impact processes and planetary interiors.