(Researchers at U of T and LG develop ‘explainable’ artificial intelligence algorithm)
2021/3/31 カナダ・トロント大学

・ トロント大学と LG AI Research Canada が、ディプレイ画面の欠陥の特定と除去を支援する「説明できる」人工知能(XAI)アルゴリズム、「Semantic Input Sampling for Explanation(SISE)」を開発。
・ 業界基準の技術の性能を超える同新アルゴリズムは、ビジネスアプリケーションに向けた AI の開発を主眼に 2019 年に展開した、LG とトロント大学による AI 共同研究活動において開発された。
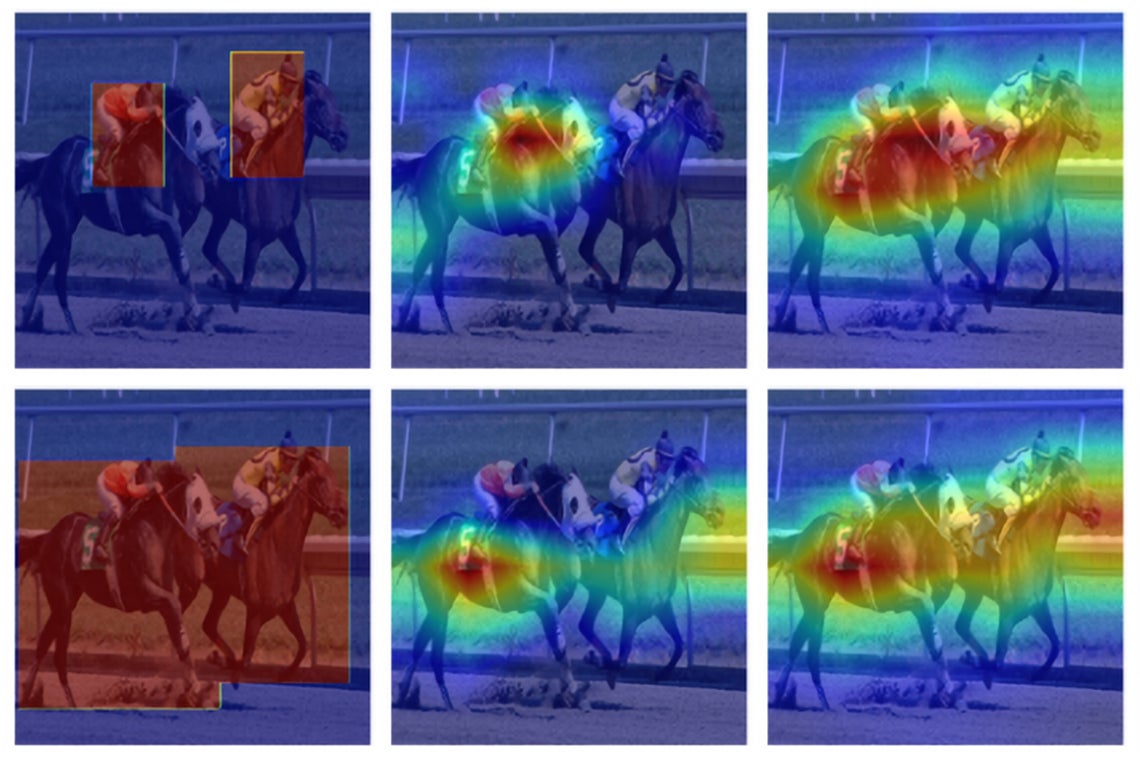
・ 自社ディスプレイ製品の欠陥を特定する機械学習モデルをすでに保有していた LG では、2 種類に大別される XAI アルゴリズム開発の方法論である Back propagation(誤差逆伝播法)と perturbation(摂動)のそれぞれの利点を組合せた新技術を要望 。トロント大学は、許容レベルのランタイムを維持しながら、欠陥の可能性を示す高解像度ヒートマップの精度を向上させた。
・ 特定のシナリオにおける問題と目的では、アルゴリズムの調整が不可欠となる。SISE による「説明できるマップ」はより容易に解釈できるため、メディカルスキャンデータの解釈等を含む、機械学習による意志決定プロセスの説明が必要となる分野での幅広いアプリケーションが可能。XAI は、機械学習における「ブラックボックス化」のアプローチの課題に対処する新興分野。
・ ブラックボックスモデルでは、ラベル付けした膨大な数の画像のトレーニングデータセットをアルゴリズムが分析し、インプット(画像)の特徴と出力(ラベル)の関連性を学習後、新規に扱う画像への正確なラベル付けを行う。 画像の特徴で認識または無視するものを機械が自ら決定するため、結論に至る根拠が不明となり、ヘルスケア、法律や保険の分野で利用する場合に問題となる。
・ 一方、意志決定を透明化した「ガラス張りのボックス」のアプローチ設計である XAI アルゴリズムでは、従来のアルゴリズムによる作業を同時に進め、それらの学習能力の有効性とレベルを調査する。また、デバッグの機会を提供してトレーニングの効率性を確認する。
・ トロント大学とのパートナーシップにおいて、LG は AI イノベーションの世界的なリーダーを目指す。今回の XAI の成果は、AI の使用により顧客満足度を高め、自社製品の機能性、製造イノベーション、サプライチェーン管理や材料発見の効率性等の様々な領域に貢献する、同社による活動を証明するもの。
URL: https://www.utoronto.ca/news/researchers-u-t-and-lg-develop-explainable-artificial-intelligence-algorithm
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
(関連情報)
35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 発表論文(フルテキスト)
Explaining Convolutional Neural Networks through Attribution-Based Input Sampling and Block-Wise
Feature Aggregation
URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.00672
Abstract
As an emerging field in Machine Learning, Explainable AI (XAI) has been offering remarkable performance in interpreting the decisions made by Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). To achieve visual explanations for CNNs, methods based on class activation mapping and randomized input sampling have gained great popularity. However, the attribution methods based on these techniques provide lower resolution and blurry explanation maps that limit their explanation power. To circumvent this issue, visualization based on various layers is sought. In this work, we collect visualization maps from multiple layers of the model based on an attribution-based input sampling technique and aggregate them to reach a fine-grained and complete explanation. We also propose a layer selection strategy that applies to the whole family of CNN-based models, based on which our extraction framework is applied to visualize the last layers of each convolutional block of the model. Moreover, we perform an empirical analysis of the efficacy of derived lower-level information to enhance the represented attributions. Comprehensive experiments conducted on shallow and deep models trained on natural and industrial datasets, using both ground-truth and model-truth based evaluation metrics validate our proposed algorithm by meeting or outperforming the state-of-the-art methods in terms of explanation ability and visual quality, demonstrating that our method shows stability regardless of the size of objects or instances to be explained.