(Eye-Controlled Soft Lens Paves Way to Soft Human-Machine Interfaces)
2019/8/2 アメリカ合衆国・カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校 (UCSD)
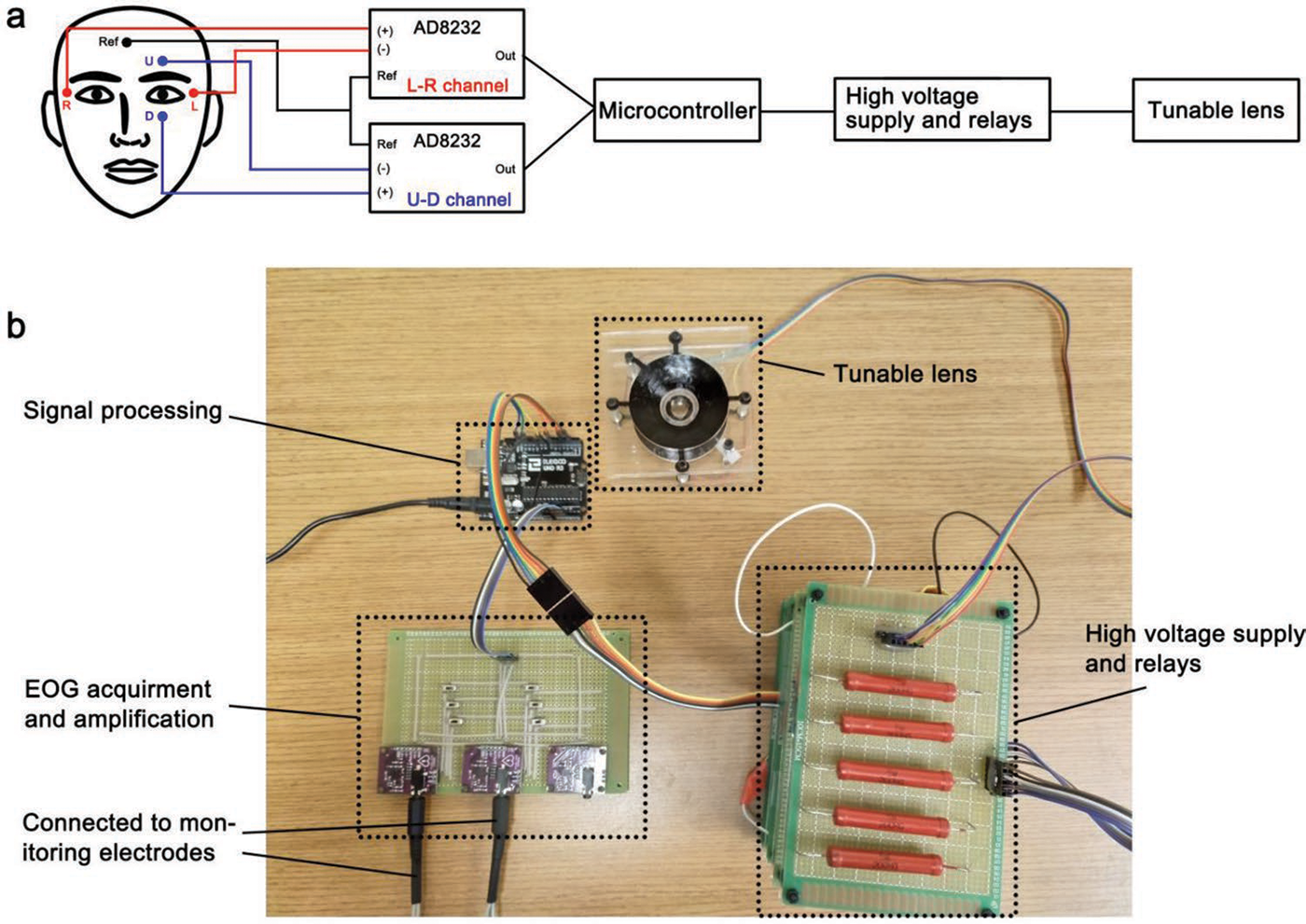
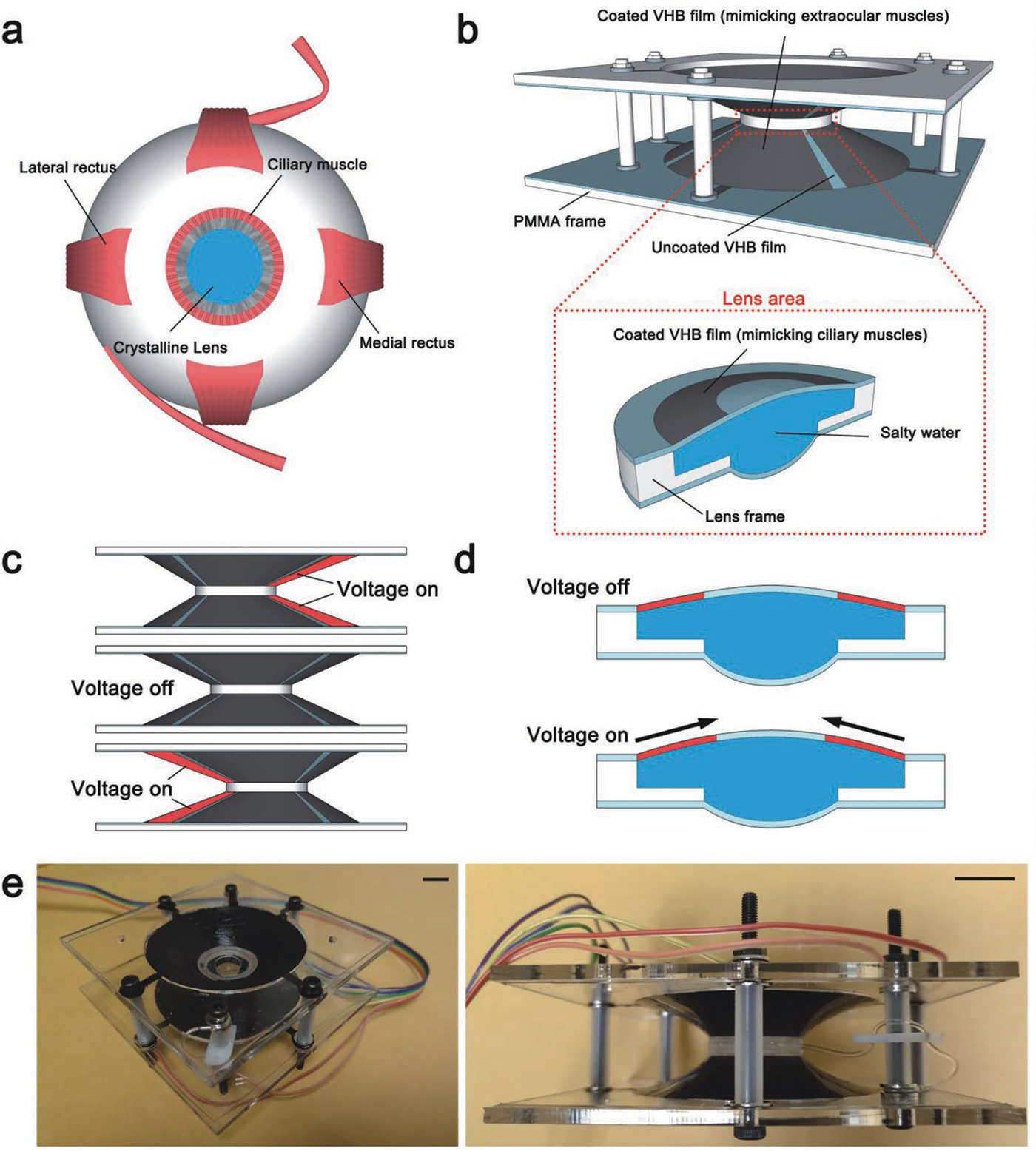
・ UCSD が、眼球の動きで制御する、ロボティックソフトレンズを開発。2 回のまばたきでズームイン・ズームアウトや上下左右への方向転換が可能。
・ 現行のヒューマン・マシーンインターフェース(HMI)では、コンピューターや固いロボティクス等の古典的なマシーンを使用している。今回の発明は、人間とソフトマシーンを結ぶインターフェースの最初の実例となる。視覚補綴、調整型メガネや VR、視力を備えたソフトロボット等のアプリケーションが考えられる。
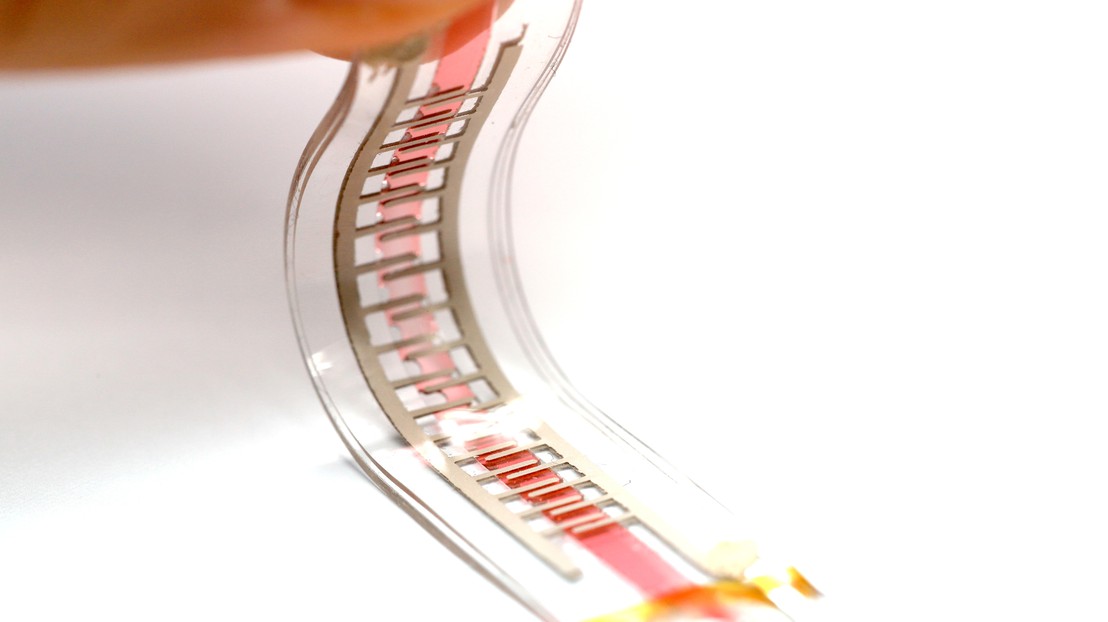
・ 同ロボティックレンズは、筋肉のような働きをする電気的に活性なポリマーフィルム 2 枚に包まれた食塩水から構成され、眼電位信号と呼ばれる、眼球の動きで発生する電気信号に反応する。眼の周囲の皮膚に配置した電極パッチがこれらの電気信号を検出し、信号プロセッサを通じてレンズに送信する。
・ 身体の信号による遠隔制御可能な柔軟な活性材料の概念実証として作製された同レンズは、電位がかかることで起こる膨張、収縮、構造変化により、視線の 4 方向と焦点を変化させる。柔軟な材料で構成されるため、焦点距離を最大で 32%変更できる。
・ 同レンズの実証では、眼球の動きで発生する電気信号で調整可能なソフトレンズを制御したが、手の動きや心拍等の他の生体信号を利用したソフトグリッパー等の制御も原理上可能と考える。
・ 本研究は、米海軍研究局(ONR)、中国国家自然科学基金(NSFC)および中国国家留学基金管理委員会(CSC)が支援した。
URL: https://ucsdnews.ucsd.edu/pressrelease/eye-controlled-soft-lens-paves-way-to-softhuman-machine-interfaces
(関連情報)
Advanced Functional Materials 掲載論文(アブストラクトのみ:全文は有料)
A Biomimetic Soft Lens Controlled by Electrooculographic Signal
URL: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/adfm.201903762
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
Abstract
Thanks to many unique features, soft robots or soft machines have been recently explored intensively to work collaboratively with human beings. Most of the previously developed soft robots are either controlled manually or by prewritten programs. In the current work, a novel human–machine interface is developed to use electrooculographic signals generated by eye movements to control the motions and the change of focal length of a biomimetic soft lens. The motion and deformation of the soft lens are achieved by the actuation of different areas of dielectric elastomer films, mimicking the working mechanisms of the eyes of human and most mammals. The system developed in the current study has the potential to be used in visual prostheses, adjustable glasses, and remotely operated robotics in the future.



