物理法則に制御を委ねることで、機械学習のエネルギー効率を向上させることができる By handing over control to the laws of physics, machine learning can be made more energy-efficient
2022-04-13 ワシントン大学セントルイス
・AIのエネルギー消費量を減らすために、ワシントン大学セントルイス校マッケルビー工学部のクリフォード・W・マーフィー教授であるシャンタヌ・チャクラバティは、新しい種類のコンピューター・メモリのプロトタイプを報告した。この研究成果は『Nature Communications』誌に掲載されました。
<関連情報>
- https://source.wustl.edu/2022/04/a-nature-driven-solution-for-more-efficient-ai/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-29320-6
ファウラーノルトハイムの動的アナログメモリを用いた適応型シナプスアレイ An adaptive synaptic array using Fowler–Nordheim dynamic analog memory
Darshit Mehta,Mustafizur Rahman,Kenji Aono &Shantanu Chakrabartty
Nature Communications. Published: 29 March 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29320-6
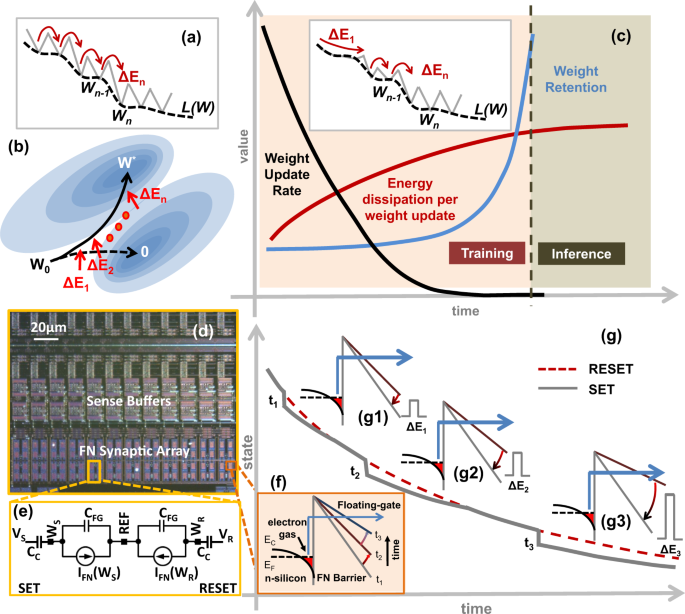
図1: 提案するシナプス記憶装置の動機と動作原理。
Abstract
In this paper we present an adaptive synaptic array that can be used to improve the energy-efficiency of training machine learning (ML) systems. The synaptic array comprises of an ensemble of analog memory elements, each of which is a micro-scale dynamical system in its own right, storing information in its temporal state trajectory. The state trajectories are then modulated by a system level learning algorithm such that the ensemble trajectory is guided towards the optimal solution. We show that the extrinsic energy required for state trajectory modulation can be matched to the dynamics of neural network learning which leads to a significant reduction in energy-dissipated for memory updates during ML training. Thus, the proposed synapse array could have significant implications in addressing the energy-efficiency imbalance between the training and the inference phases observed in artificial intelligence (AI) systems.