(Researchers reach quantum networking milestone in real-world environment)
2021-10-08 アメリカ合衆国・オークリッジ国立研究所(ORNL)
・ ORNL、スタンフォード大学およびパデュー大学が、光ファイバーを利用した量子ローカルエリアネットワーク(QLAN)で量子もつれ配送を実証。
・ 量子超越性を実現するための実際のネットワークでの展開を目指し、量子ネットワーキング・アプリケーションの実証に不可欠な基礎ツールと構成要素の開発を目標とする。
・ 2 つの光子の重ね合わせで起こる強力な量子的相関を利用した量子通信プロトコルの一つである遠隔状態準備(remote state preparation(RSP))を全 QLAN リンクに適用し、量子もつれをベースとした量子情報通信のスケーラビリティーを実証。RSP は、量子もつれと古典的通信方法により、もつれ光子ペアの半分を計測し、残り半分を良好な量子状態に効果的に変換して情報をエンコードするもの。
・ ORNL キャンパス内の 3 棟のビル内の離れた 3 ヶ所の研究室(アリス、ボブおよびチャーリー)の各ノードをつなぎ、ORNL の既設光ファイバーを通じてアリス・光子源の研究室からボブとチャーリーに光子による量子もつれを配送した。
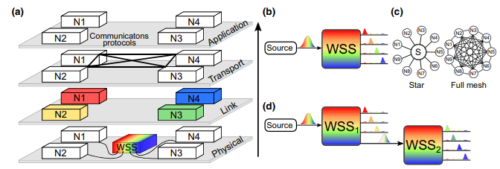
・ 量子相関に干渉する従来の信号増幅器の代わりに、QLAN を切断することなくネットワークユーザーに量子リソースの割り当てを切り替える波長選択スイッチを採用。ネットワーク速度やセキュリティープロトコルを損なわずにトラフィック経路を切り替えることで、光ファイバーの損傷等の予期せぬ現象への対応を可能にする、ビルトインのフォールト・トレランスを提供する。
・ また、量子ネットワークで重要な各ノードの活動のタイミングの同期に汎用性のある安価な GPS を活用。ボブの研究室に設置した GPS アンテナを利用して各ノードで信号を共有し、GPS ベースクロックの数ナノ秒での同期を維持。光子検出器で計測した量子もつれ光子の正確な到着のタイミングをQLAN から従来のネットワークに転送し、3 ヶ所の研究室からの高品質データをコンパイルした。
・ 量子インターネット開発における次の主要なステップは、QLAN を他の量子ネットワークに接続すること。今後の実験では、ネットワークのノイズ源を低減して QLAN のサービス品質(QoS)を向上するためのより高度なタイミング同期に注視する。
・ 本研究は、Early Career Research Program、Transparent Optical Quantum Networks for Distributed
Science Program および Basic Energy Science program’s Materials Sciences and Engineering Division
を通 じ、米国エネルギー省(DOE)科学局が支援 した。また、ORNL の Intelligence Community Postdoctoral Research Fellowship Program および米国立科学財団(NSF)の Quantum Information Science and Engineering Network が追加的な支援を提供した。
URL: https://www.ornl.gov/news/researchers-reach-quantum-networking-milestone-real-world-environment
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
(関連情報)
PRX Quantum 掲載論文(フルテキスト)
Reconfigurable Quantum Local Area Network Over Deployed Fiber
URL: https://journals.aps.org/prxquantum/pdf/10.1103/PRXQuantum.2.040304
Abstract
Practical quantum networking architectures are crucial for scaling the connection of quantum resources. Yet quantum network testbeds have thus far underutilized the full capabilities of modern lightwave communications, such as flexible-grid bandwidth allocation. In this work, we implement flex-grid entanglement distribution in a deployed network for the first time, connecting nodes in three distinct campus buildings time synchronized via the Global Positioning System. We quantify the quality of the distributed polarization entanglement via log-negativity, which offers a generic metric of link performance in entangled bits per second. After demonstrating successful entanglement distribution for two allocations of our eight dynamically reconfigurable channels, we realize the first deployed fiber network demonstration of remote state preparation (RSP), a fundamental quantum communications protocol with utility for performing remote private “blind” quantum computing. We further demonstrate RSP not only at one location but over three nodes in three locations. In general, our results highlight an advanced paradigm for managing entanglement resources in quantum networks of ever-increasing complexity and service demands.