2025-06-02 パシフィック・ノースウェスト国立研究所(PNNL)
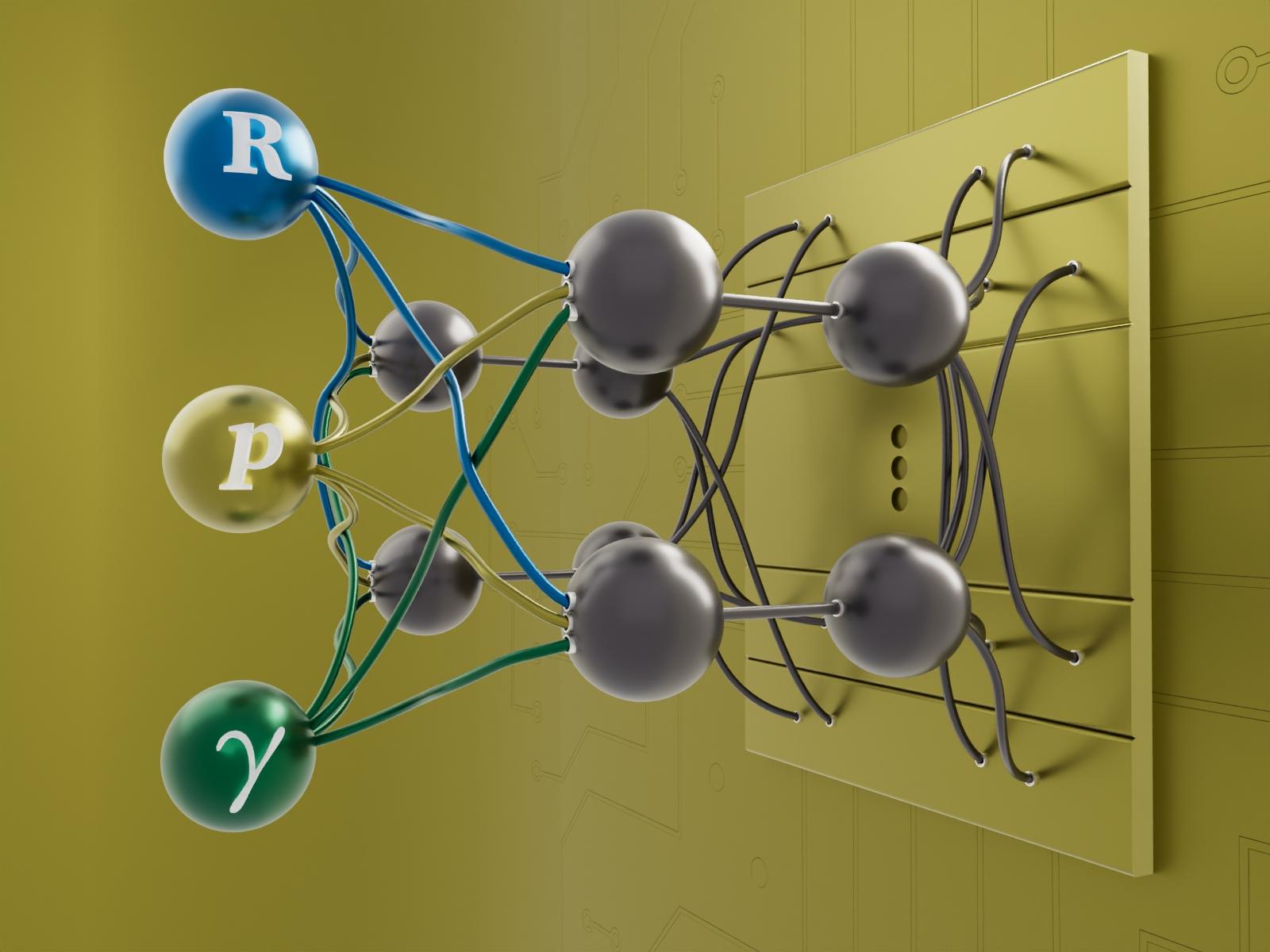
The VNet neural network can be used to rapidly generate downfolded Hamiltonians that capture electron correlation effects in small dimensionality spaces.
(Image by Ben Watson | Pacific Northwest National Laboratory)
<関連情報>
- https://www.pnnl.gov/publications/neural-networks-evaluating-effective-interactions
- https://journals.aps.org/prresearch/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevResearch.6.043287
ニューラルネットワークモデルによる低次元空間での効果的な多体相互作用 Effective many-body interactions in reduced-dimensionality spaces through neural network models
Senwei Liang, Karol Kowalski, Chao Yang, and Nicholas P. Bauman
Physical Review Research Published: 17 December, 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevResearch.6.043287
Abstract
Accurately describing properties of challenging problems in physical sciences often requires complex mathematical models that are unmanageable to tackle head on. Therefore, developing reduced-dimensionality representations that encapsulate complex correlation effects in many-body systems is crucial to advance the understanding of these complicated problems. However, a numerical evaluation of these predictive models can still be associated with a significant computational overhead. To address this challenge, in this paper we discuss a combined framework that integrates recent advances in the development of active-space representations of coupled cluster (CC) downfolded Hamiltonians with neural network approaches. The primary objective of this effort is to train neural networks to eliminate the computationally expensive steps required for evaluating hundreds or thousands of Hugenholtz diagrams, which correspond to multidimensional tensor contractions necessary for evaluating a many-body form of downfolded effective Hamiltonians. Using small molecular systems (the H2O and HF molecules) as examples, we demonstrate that training neural networks employing effective Hamiltonians for a few nuclear geometries of molecules can accurately interpolate or extrapolate their forms to other geometrical configurations characterized by different intensities of correlation effects. We also discuss differences between effective interactions that define CC downfolded Hamiltonians with those of bare Hamiltonians defined by Coulomb interactions in the active spaces.