2024-03-25 オークリッジ国立研究所(ORNL)
<関連情報>
- https://www.ornl.gov/news/dealing-stress-large-scale-additive-manufacturing
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212827123009861
大規模Ti-6Al-4Vワイヤーアーク積層造形における残留応力蓄積 Residual stress accumulation in large-scale Ti-6Al-4V wire-arc additive manufacturing
Ritin Mathews, Jaydeep Karandikar, Christopher Tyler, Scott Smith
Procedia CIRP Available online:1 February 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2023.09.247
Abstract
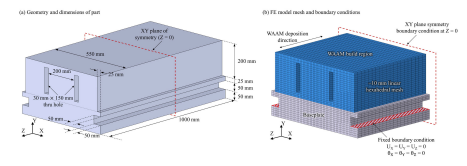
Large-scale additive manufacturing (AM) is of interest in the manufacturing industry to produce components of dimensions on the order of hundreds of millimeters to meters in scale. Wire-arc AM (WAAM) of Ti-6Al-4V (Ti64) is an attractive technique for large-scale AM in the aerospace industry, give the high strength-to-weight ratio of the material and high deposition rate of the process. However, due to the large scale, significant distortion and residual stresses are developed in the material during deposition and cooling, potentially leading to part failure. WAAM of a prototypical large-scale Ti64 machine tool component is studied in this work via finite element analysis (FEA). Element activation/deactivation technique is employed to simulate deposition and the resulting distortion and residual stress (RS) predictions are analyzed to evaluate the possibility of crack formation. Significant distortion (∼10 mm) and RS (>1300 MPa) is predicted, suggesting the formation of cracks and possible crack propagation into the build region. Incorporation of fillets significantly reduces RS concentration regions, thus reducing the possibility of part failure. Material deposition sequence also affects the RS pattern in the build.