2023-05-01 ヒューストン大学(UH)
このアプローチにより、温度範囲を横断して作動する高性能熱電モジュールの開発が加速されると期待される。熱電材料は、廃熱や工業プロセスによって発生する熱を電気に変換するための潜在的なクリーンエネルギー源として注目されており、この新しいアプローチはその可能性を引き出すことができる。
<関連情報>
- https://uh.edu/news-events/stories/2023/may-2023/05012023-silver-nanoparticles-thermoelectricity.php
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41560-023-01245-4
高性能熱電モジュール設計のためのAgナノ粒子の低温焼結法 Low-temperature sintering of Ag nanoparticles for high-performance thermoelectric module design
Li Yin,Fan Yang,Xin Bao,Wenhua Xue,Zhipeng Du,Xinyu Wang,Jinxuan Cheng,Hongjun Ji,Jiehe Sui,Xingjun Liu,Yumei Wang,Feng Cao,Jun Mao,Mingyu Li,Zhifeng Ren & Qian Zha
Nature Energy Published:01 May 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-023-01245-4
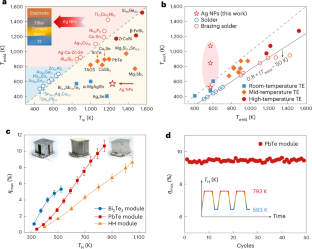
Abstract
To facilitate the development of thermoelectric modules for various operating temperature ranges, a connection technology that is suitable for heat-sensitive thermoelectric materials and capable of realizing both low-temperature connections and high-temperature service is required. Here we use low-temperature sintering of silver nanoparticles as an approach to connect the electrode and metallization layer of low- (Bi2Te3-based), medium- (PbTe-based) and high-temperature (half-Heusler-based) thermoelectric modules. Owing to the low melting point of Ag nanoparticles and the high stability in the sintered bulk, the processing temperature of the module is decoupled from the operating temperature, avoiding welding thermal stress. We demonstrate a conversion efficiency of ~11% at the temperature difference of 550 K for the PbTe-based module. Additionally, the module’s performance remains nearly unchanged throughout thermal cycling between hot-side temperatures of 593 and 793 K for 50 cycles. Our work accelerates the development of advanced modules for thermoelectric power generation.