2023-01-17 米国国立再生可能エネルギー研究所(NREL)
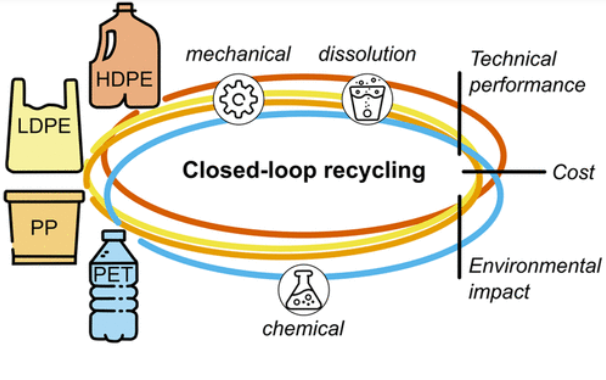
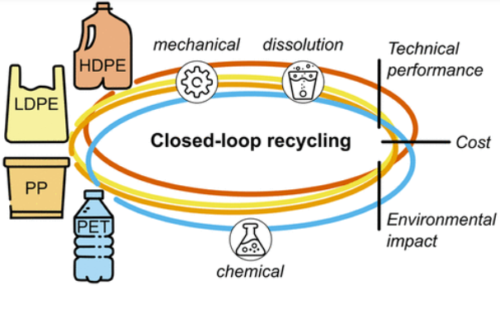
研究者たちは、機械的または化学的処理によってプラスチックを再利用し、化石燃料由来の新材料を必要としない閉ループリサイクルのための様々な技術を比較しました。研究者たちは、材料の品質や保存性などの技術的な指標に加え、エネルギー使用量や温室効果ガス排出量などの環境的な指標についても検討しました。
ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 誌に掲載された「Technical, economic, and environmental comparison of closed-loop recycling technologies for common plastics」の主執筆者である Taylor Uekert 氏は、「リサイクルに投資しようとする企業にとって、コストが主要因の1つ(主要因でないにしても)であることは分かっています」と述べています。「しかし、この地球上の私たちの生活にとって同様に重要なものが他にもあることを忘れてはならないと思います。
この論文では、ポリエチレンテレフタレート(PET)と3種類のポリオレフィン(高密度ポリエチレン(HDPE)、低密度ポリエチレン(LDPE)、ポリプロピレン(PP))に対するクローズドループ・リサイクル技術の効果について概説しています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.nrel.gov/news/press/2023/news-release-nrel-develops-systematic-framework-to-compare-performance-of-plastics-recycling-approaches.html
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c05497
一般的なプラスチックのクローズドループリサイクル技術の技術、経済、および環境比較 Technical, Economic, and Environmental Comparison of Closed-Loop Recycling Technologies for Common Plastics
Taylor Uekert, Avantika Singh, Jason S. DesVeaux, Tapajyoti Ghosh, Arpit Bhatt, Geetanjali Yadav, Shaik Afzal, Julien Walzberg, Katrina M. Knauer, Scott R. Nicholson, Gregg T. Beckham, and Alberta C. Carpenter
ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering Published:January 12, 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c05497
Abstract
Over 400 million metric tons of plastic waste are generated globally each year, resulting in pollution and lost resources. Recycling strategies can recapture this wasted material, but there is a lack of quantitative and transparent data on the capabilities and impacts of these processes. Here, we develop a data set of material quality, material retention, circularity, contamination tolerance, minimum selling price, greenhouse gas emissions, energy use, land use, toxicity, waste generation, and water use metrics for closed-loop polymer recycling technologies, including mechanical recycling and solvent-based dissolution of polyethylene, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and polypropylene, as well as enzymatic hydrolysis, glycolysis, and vapor methanolysis of PET. Mechanical recycling and PET glycolysis display the best economic (9%–73% lower than competing technologies) and environmental (7%–88% lower) performances, while dissolution, enzymatic hydrolysis, and methanolysis provide the best recyclate material qualities (2%–27% higher). We identify electricity, steam, and organic solvents as top process contributors to these metrics and apply sensitivity and multicriteria decision analyses to highlight key future research areas. The estimates derived in this work provide a quantitative baseline for comparing and improving recycling technologies, can help reclaimers identify optimal end-of-life routes for given waste streams, and serve as a framework for assessing future innovations.