このアルゴリズムにより、太陽電池の新材料の発見が期待される。 Team’s algorithm could lead to pivotal discovery of new materials for solar cells.
2022-08-31 アルゴンヌ国立研究所(ANL)
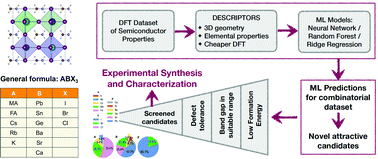
研究チームは、機械学習法を用いて、ハライドペロブスカイトと呼ばれる一群の材料の太陽エネルギー特性を評価した。
研究チームは、数百種類のハライドペロブスカイト組成のデータでその手法を学習させ、その後、テストケースとして18,000種類以上の組成に適用しました。この手法では、安定性、太陽光を吸収する能力、欠陥があっても簡単に壊れない構造などの主要な特性について、これらの組成物を評価した。計算結果は、科学文献にある関連データとよく一致した。また、この結果から、さらに研究を進める価値のある組成物が約400種類に絞られた。
候補リストには、すでに研究されている化合物や、誰も研究したことのない化合物、さらには当初の18,000化合物の中に含まれていなかった化合物も含まれている。
<関連情報>
- https://www.anl.gov/article/soaking-up-the-sun-with-artificial-intelligence
- https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2022/EE/D1EE02971A
データ駆動による新規ハライドペロブスカイト合金の設計 Data-driven design of novel halide perovskite alloys
Arun Mannodi-Kanakkithodi and Maria K. Y. Chan
Energy & Environmental Science Published:21 Mar 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EE02971A
Abstract
The great tunability of the properties of halide perovskites presents new opportunities for optoelectronic applications as well as significant challenges associated with exploring combinatorial chemical spaces. In this work, we develop a framework powered by high-throughput computations and machine learning for the design and prediction of mixed cation halide perovskite alloys. In a chemical space of ABX3 perovskites with a selected set of options for A, B, and X species, pseudo-cubic structures with B-site mixing are simulated using density functional theory (DFT) and several properties are computed, including stability, lattice constant, band gap, vacancy formation energy, refractive index, and optical absorption spectrum, using both semi-local and hybrid functionals. Neural networks (NN) are used to train predictive models for every property using tabulated elemental properties of A, B, and X site species as descriptors. Starting from a DFT dataset of 229 points, we use the trained NN models to predict the structural, energetic, electronic, and optical properties of an extensive dataset of 17 955 compounds, and perform high-throughput screening in terms of stability, band gap, and defect tolerance, to obtain 392 promising compounds that are ranked as potential absorbers according to their photovoltaic figure of merit. Compositional trends in the screened set of attractive mixed cation halide perovskites are revealed and additional computations are performed on selected compounds. The data-driven design framework developed here is promising for designing novel mixed compositions and can be extended to a wider perovskite chemical space in terms of A, B, and X species, different kinds of mixing at the A, B, or X sites, non-cubic phases, and other properties of interest.