将来の電子・熱電変換技術の設計に役立つ研究です。 Research will benefit design of future electronic and thermoelectric technologies
2022-06-08 カリフォルニア大学校アーバイン校(UCI)
研究者らは、結晶中の欠陥や界面によってフォノンがどのように散乱されるかを調べるため、カリフォルニア大学アーバイン校の材料研究所にある透過型電子顕微鏡で、振動電子エネルギー損失分光法を用いてシリコン-ゲルマニウムの単一量子ドット付近のフォノンの動的挙動を探りました。このプロジェクトの成果は、Nature誌に掲載されました。
<関連情報>
- https://news.uci.edu/2022/06/08/uci-scientists-observe-effects-of-heat-in-materials-with-atomic-resolution/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-04736-8
電子顕微鏡によるフォノンダイナミクスのナノスケール画像化 Nanoscale imaging of phonon dynamics by electron microscopy
Chaitanya A. Gadre,Xingxu Yan,Qichen Song,Jie Li,Lei Gu,Huaixun Huyan,Toshihiro Aoki,Sheng-Wei Lee,Gang Chen,Ruqian Wu & Xiaoqing Pan
Nature Published:08 June 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04736-8
Abstract
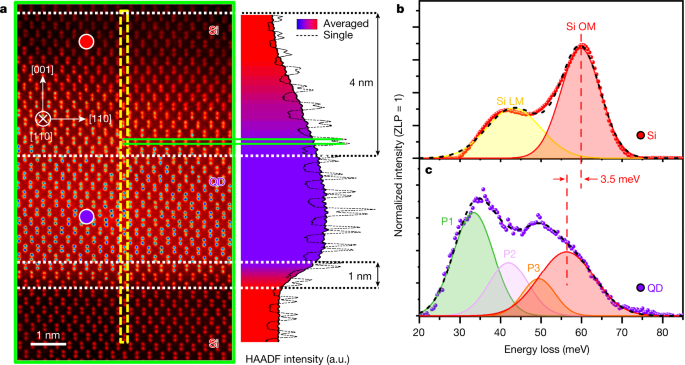
Spatially resolved vibrational mapping of nanostructures is indispensable to the development and understanding of thermal nanodevices1, modulation of thermal transport2 and novel nanostructured thermoelectric materials3,4,5. Through the engineering of complex structures, such as alloys, nanostructures and superlattice interfaces, one can significantly alter the propagation of phonons and suppress material thermal conductivity while maintaining electrical conductivity2. There have been no correlative experiments that spatially track the modulation of phonon properties in and around nanostructures due to spatial resolution limitations of conventional optical phonon detection techniques. Here we demonstrate two-dimensional spatial mapping of phonons in a single silicon–germanium (SiGe) quantum dot (QD) using monochromated electron energy loss spectroscopy in the transmission electron microscope. Tracking the variation of the Si optical mode in and around the QD, we observe the nanoscale modification of the composition-induced red shift. We observe non-equilibrium phonons that only exist near the interface and, furthermore, develop a novel technique to differentially map phonon momenta, providing direct evidence that the interplay between diffuse and specular reflection largely depends on the detailed atomistic structure: a major advancement in the field. Our work unveils the non-equilibrium phonon dynamics at nanoscale interfaces and can be used to study actual nanodevices and aid in the understanding of heat dissipation near nanoscale hotspots, which is crucial for future high-performance nanoelectronics.



