2024-02-08 ロスアラモス国立研究所(LANL)
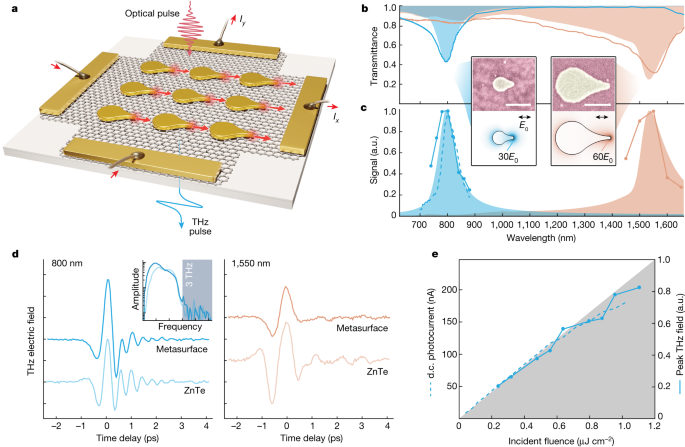
◆ナノアンテナは光を捕捉し集中させる。研究チームは、グラフェン上の原子薄層に非対称なナノサイズの金構造を設計し、製造した。これらの金構造は、光波を捕捉し集中させる方法に基づいて「ナノアンテナ」と呼ばれ、光学的な「ホットスポット」を形成する。ナノアンテナの尖った先端にのみホットスポットがあり、励起されたホット電子が流れる経路が生じる。
◆これらの構造は、ピコ秒未満の応答速度でホットスポットとナノスケールの電荷流の振幅、位置、方向を制御する簡単な方法を提供する。
<関連情報>
- https://discover.lanl.gov/news/0207-nanoscale-light-driven-technology/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07037-4
光で駆動するナノスケールのベクトル電流 Light-driven nanoscale vectorial currents
Jacob Pettine,Prashant Padmanabhan,Teng Shi,Lauren Gingras,Luke McClintock,Chun-Chieh Chang,Kevin W. C. Kwock,Long Yuan,Yue Huang,John Nogan,Jon K. Baldwin,Peter Adel,Ronald Holzwarth,Abul K. Azad,Filip Ronning,Antoinette J. Taylor,Rohit P. Prasankumar,Shi-Zeng Lin & Hou-Tong Chen
Nature Published:07 February 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07037-4
Abstract
Controlled charge flows are fundamental to many areas of science and technology, serving as carriers of energy and information, as probes of material properties and dynamics1 and as a means of revealing2,3 or even inducing4,5 broken symmetries. Emerging methods for light-based current control5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16 offer particularly promising routes beyond the speed and adaptability limitations of conventional voltage-driven systems. However, optical generation and manipulation of currents at nanometre spatial scales remains a basic challenge and a crucial step towards scalable optoelectronic systems for microelectronics and information science. Here we introduce vectorial optoelectronic metasurfaces in which ultrafast light pulses induce local directional charge flows around symmetry-broken plasmonic nanostructures, with tunable responses and arbitrary patterning down to subdiffractive nanometre scales. Local symmetries and vectorial currents are revealed by polarization-dependent and wavelength-sensitive electrical readout and terahertz (THz) emission, whereas spatially tailored global currents are demonstrated in the direct generation of elusive broadband THz vector beams17. We show that, in graphene, a detailed interplay between electrodynamic, thermodynamic and hydrodynamic degrees of freedom gives rise to rapidly evolving nanoscale driving forces and charge flows under the extremely spatially and temporally localized excitation. These results set the stage for versatile patterning and optical control over nanoscale currents in materials diagnostics, THz spectroscopies, nanomagnetism and ultrafast information processing.