2022-11-14 ローレンスリバモア国立研究所(LLNL)
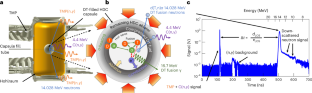
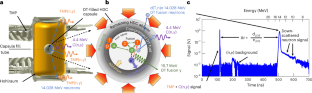
この研究は、高収率燃焼・点火慣性閉じ込め核融合実験(ICF)の中性子エネルギー測定から、発生する平均中性子エネルギーが、熱平衡状態にある重水素・三重(D-T)プラズマの予想よりも高い事を示している。
<関連情報>
- https://www.llnl.gov/news/llnl-researchers-observe-ions-behave-differently-fusion-reactions
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-022-01809-3
燃焼プラズマにおける超熱的なイオン分布の証拠 Evidence for suprathermal ion distribution in burning plasmas
E. P. Hartouni,A. S. Moore,A. J. Crilly,B. D. Appelbe,P. A. Amendt,K. L. Baker,D. T. Casey,D. S. Clark,T. Döppner,M. J. Eckart,J. E. Field,M. Gatu-Johnson,G. P. Grim,R. Hatarik,J. Jeet,S. M. Kerr,J. Kilkenny,A. L. Kritcher,K. D. Meaney,J. L. Milovich,D. H. Munro,R. C. Nora,A. E. Pak,J. E. Ralph,H. F. Robey,J. S. Ross,D. J. Schlossberg,S. M. Sepke,B. K. Spears,C. V. Young & A. B. Zylstra
Nature Physics Published:14 November 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-022-01809-3
Abstract
At the National Ignition Facility, inertial confinement fusion experiments aim to burn and ignite a hydrogen plasma to generate a net source of energy through the fusion of deuterium and tritium ions. The energy deposited by α-particles released from the deuterium–tritium fusion reaction plays the central role in heating the fuel to achieve a sustained thermonuclear burn. In the hydrodynamic picture, α-heating increases the temperature of the plasma, leading to increased reactivity because the mean ion kinetic energy increases. Therefore, the ion temperature is related to the mean ion kinetic energy. Here we use the moments of the neutron spectrum to study the relationship between the ion temperature (measured by the variance in the neutron kinetic energy spectrum) and the ion mean kinetic energy (measured by the shift in the mean neutron energy). We observe a departure from the relationship expected for plasmas where the ion relative kinetic energy distribution is Maxwell–Boltzmann, when the plasma begins to burn. Understanding the cause of this departure from hydrodynamic behaviour could be important for achieving robust and reproducible ignition.