2022-07-11 ドイツ連邦共和国・ヘルマン・フォン・ヘルムホルツ協会(HGF)
・ ヘルムホルツセンターポツダム(GFZ Potsdam)等から成る研究チームが、ペロブスカイト-シリコンタンデム型(PST)PV モジュールに関するライフサイクルアセスメント(LCA)を報告。
・ シリコンセルの上にペロブスカイトセルを積層するタンデムシステムでは、発電力を最大化させ、現在は 31%を超えるエネルギー変換効率を達成している。標準的なシリコン技術に比べて発電量が多いため、世界の PV 導入を促進することが期待されている
・ PV モジュールの環境への影響の理解は、より持続可能な太陽エネルギーシステムの設計に不可欠であるが、これまでの PST PV モジュールの LAC では研究所や試験施設のデータを利用していた。
・ 今回、Oxford PV が提供する、ドイツ国内の大量生産ラインの PST PV モジュールとプロセスデータに基づき、工業製造された PST モジュールについて、地球温暖化ポテンシャル、水の消費量、人間と海洋に対する毒性、金属の使用等を含む、製品開発から出荷までの包括的な LCA を初めて実施。
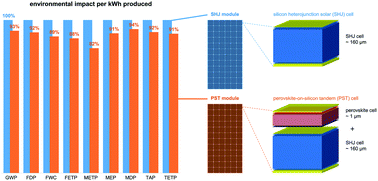
・ 結論として、製品寿命 25 年間において、従来のシリコンヘテロ接合モジュールに比べ、革新的なPST PV モジュールでは環境への影響が 6~18%低いことを確認。LCA で対象とした PST PV モジュールでは、その 22 年間における発電量がシリコンヘテロ接合 PV モジュールによる 25 年間の発電量と同等となる。
・ PST PV モジュールの高いエネルギー変換効率は、ペロブスカイト材料やプロセスの追加による環境への影響を補うこと、また、 PST PV モジュールの環境性能は、シリコンウェハーの製造に消費するエネルギーに大きく影響されることもわかった。
・ 家庭、企業、産業の脱炭素化において PV は重要な役割を担うことが期待され、費用対効果と信頼性が高く、持続可能なエネルギーを提供する手段として導入が進んでいる。
・ 世界の PV 発電導入容量は 2002 年の 2GW から 2022 年には 1TW (1,000GW) 超に増加しており、各国が気候変動目標とエネルギー安全保障の需要を満たすことを目指す中、今後数十年間において大幅な増加が予想される。
URL: https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=23891&sprache=en&seitenid=74699
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
関連情報
Sustainable Energy & Fuels 掲載論文(フルテキスト)
New insights into the environmental performance of perovskite-on-silicon tandem solar cells - a
life cycle assessment of industrially manufactured modules
URL: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2022/SE/D2SE00096B
Abstract
LCA studies of perovskite-on-silicon tandem (PST) cells have so far been heavily reliant on laboratory data and process data from test facilities to project environmental impacts, producing results that differ significantly from one another. This paper reports on potential environmental impacts of an industrially manufactured PST module. Based on process data from a volume manufacturing line in Brandenburg, Germany, a comprehensive life cycle assessment (LCA) was performed using the ReCiPe 2016 v1.1 method. The production of one module was estimated with a global warming potential (GWP) of 434 kg CO2 eq., terrestrial ecotoxicity potential of 598 kg 1,4-DB eq., freshwater consumption (FWC) of 14 m3, and fossil and metal depletion potential (FDP and MDP) of 164 kg oil eq. and 2034 g Cu eq., respectively. In line with other studies, the environmental performance of the PST module was largely influenced by the amount of energy consumed in the course of production, making the silicon wafer production the determining process step in most impact categories considered. Exceptions were found with the metal depletion potential (MDP) and terrestrial ecotoxicity potential (TETP), where copper, aluminum and float glass implemented in the cell manufacturing and module production process decisively determined the impacts of production. The built-in lead, on the other hand, had no significant influence on the result of the toxicity-specific impact categories in ReCiPe, even if complete lead emission was assumed. The results were also analysed and compared to those of a silicon hetero-junction solar cell (SHJ) module, modelled analogously to the PST production process. While we found the overall environmental impact of the PST module per piece to be higher than that of the SHJ module in most impact categories (up to 7%) due to the additional process steps, a comparison made on the basis of kW h produced shows advantages for the PST module with 6–18% across all impact categories, as a higher efficiency overcompensates the higher environmental burden of production, assuming the same lifetime for both modules.