2024-05-08 NASA
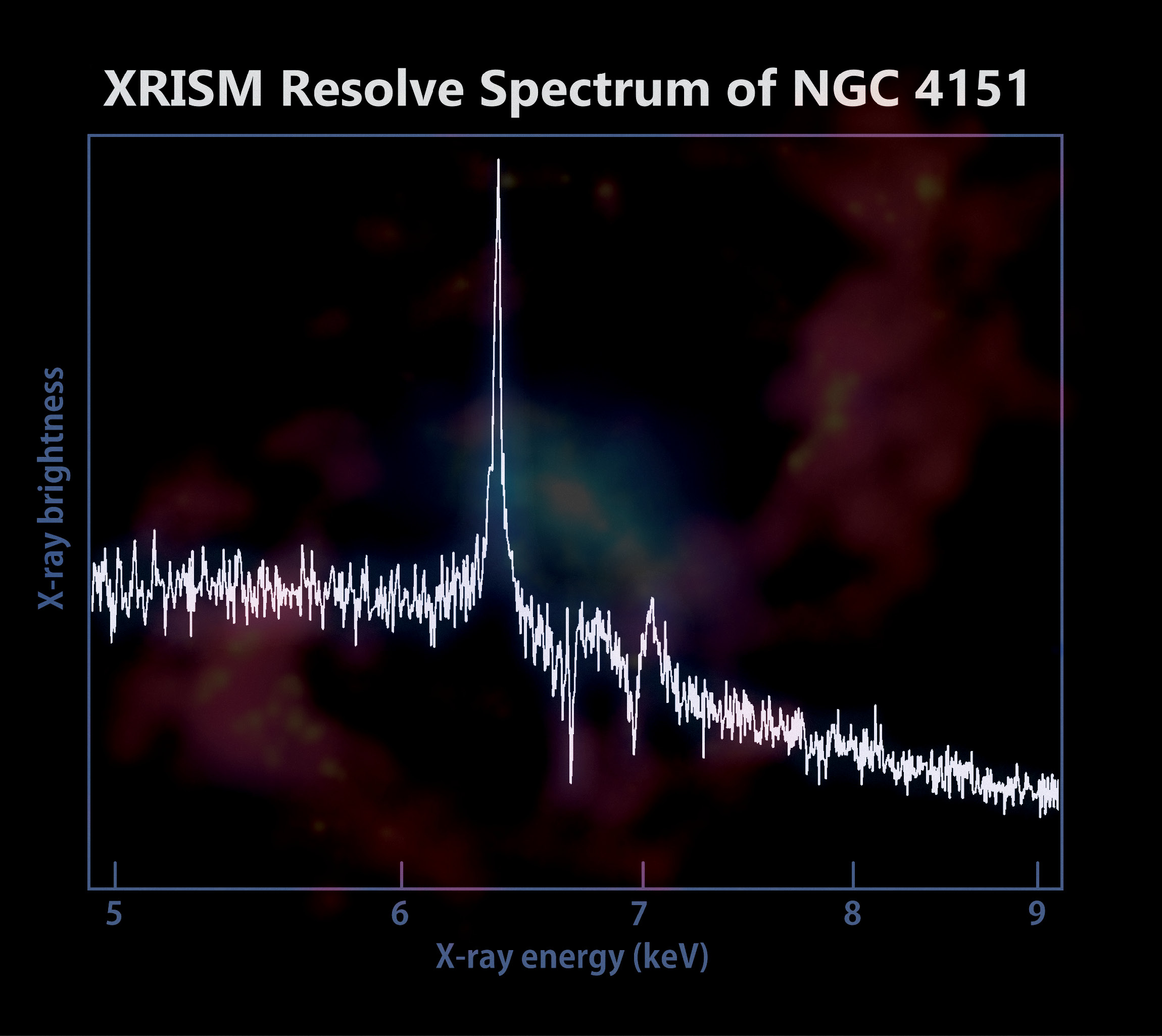 The Resolve instrument aboard XRISM (X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission) captured data from the center of galaxy NGC 4151, where a supermassive black hole is slowly consuming material from the surrounding accretion disk. The resulting spectrum reveals the presence of iron in the peak around 6.5 keV and the dips around 7 keV, light thousands of times more energetic that what our eyes can see. Background: An image of NGC 4151 constructed from a combination of X-ray, optical, and radio light.
The Resolve instrument aboard XRISM (X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission) captured data from the center of galaxy NGC 4151, where a supermassive black hole is slowly consuming material from the surrounding accretion disk. The resulting spectrum reveals the presence of iron in the peak around 6.5 keV and the dips around 7 keV, light thousands of times more energetic that what our eyes can see. Background: An image of NGC 4151 constructed from a combination of X-ray, optical, and radio light.
Spectrum: JAXA/NASA/XRISM Resolve. Background: X-rays, NASA/CXC/CfA/J.Wang et al.; optical, Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes, La Palma/Jacobus Kapteyn Telescope; radio, NSF/NRAO/VLA
日本主導のXRISM(X線イメージング・分光ミッション)は、2024年2月から科学観測を開始し、銀河NGC 4151の中心にある巨大ブラックホールを研究しました。NASAのプロジェクト科学者ブライアン・ウィリアムズ氏は「XRISMのResolve装置はブラックホール周辺の詳細なスペクトルを捉えました。ピークやディップは化学指紋のようなもので、どの元素が存在するかや物質がブラックホールに近づく過程を示す手がかりになります」と述べています。
Resolve装置のスペクトルでは、約6.5keVでの鉄のピークや約7keVでのディップが観測されました。これにより、周囲の降着円盤やトーラスに存在する鉄の位置が明らかになり、ブラックホールに近い領域での活動や鉄の存在が確認されました。
<関連情報>



