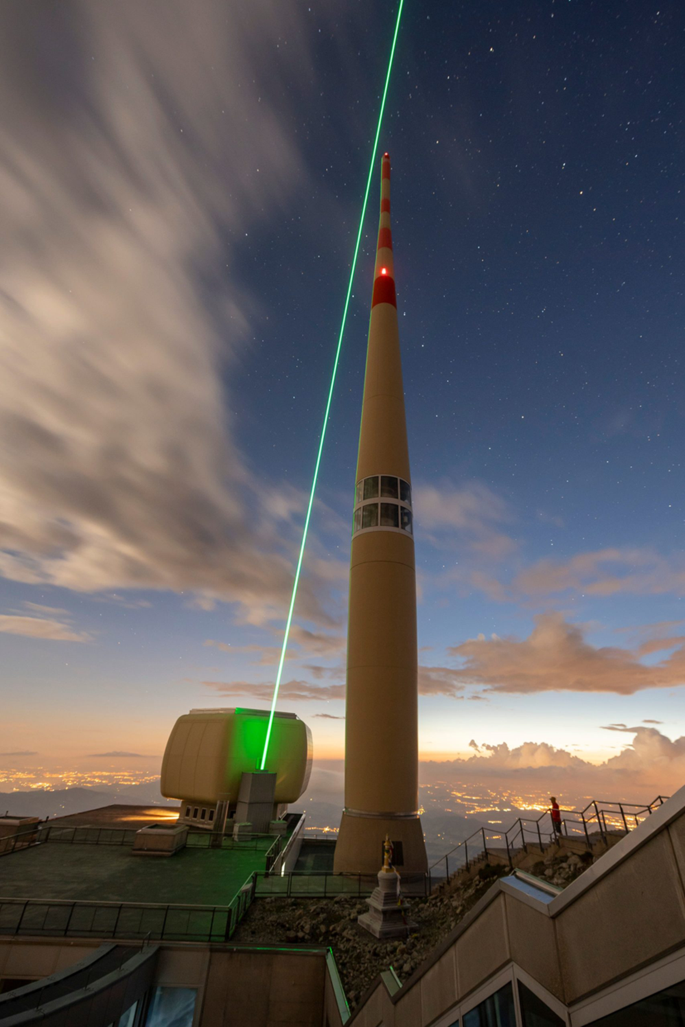
EPFLを含む欧州コンソーシアムは、スイスのゼンティス山頂に設置された高出力レーザーを用いて、雷を誘導することに成功しました。 A European consortium involving EPFL has managed to guide lightning using a high-power laser installed at the top of Mount Säntis in Switzerland.
2023-01-20 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
◆パリ理工科大学(EPFL)、HEIG-VD工学部、TRUMPF科学レーザー(ミュンヘン)からなる欧州コンソーシアムは、レーザー避雷針またはLLRという有望な代替策を開発しました。アッペンツェルのゼンティス山頂でLLRをテストした結果、研究者たちはその実現可能性を証明することができました。この避雷針は、天候が悪いときでも数十メートルにわたって雷をよけることができる。この研究成果は、学術誌『Nature Photonics』に掲載されました。
◆高強度レーザーパルスを使い、導電性のある電離した空気の流路を生成することで、LLRのビームに沿って雷を誘導することに成功しました。従来の避雷針を上方に延長することで、実質的に避雷針の高さと保護する面積を増やすことができた。LLRプロジェクトでは、平均出力1キロワット、1パルス1ジュール、1パルス1ピコ秒の新しいレーザーが開発されました。トルンプの科学レーザーが設計したこのロッドは、幅1.5m、長さ8m、重さ3トン以上。
◆LLRのテラワットレーザーは、Säntis山頂(標高2,502m)で、Swisscomが所有する高さ124mの通信タワーの近辺でテストされ、EPFLとHEIG-VD / HES-SOが雷観測のために計測を行った。この電波塔はヨーロッパの雷のホットスポットの1つで、年間約100回落雷しています。
◆EPFLは、工学部のFarhad Rachidiが所長を務める電磁両立性ラボ(EMC)からこのプロジェクトに貢献しました。EMCの研究者は、上向き雷放電の開始を研究し、HEIG-VD/HES-SOと協力して雷観測のための実験設備を展開しました。実験設備は、タワー上の雷電流計測、電磁界アンテナ、X線センサー、高速度ビデオカメラ、雷放電を画像化する干渉計システムなどで構成されています。
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/deflecting-lightning-with-a-laser-lightning-rod-2/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-022-01139-z
レーザー誘導雷 Laser-guided lightning
Aurélien Houard,Pierre Walch,Thomas Produit,Victor Moreno,Benoit Mahieu,Antonio Sunjerga,Clemens Herkommer,Amirhossein Mostajabi,Ugo Andral,Yves-Bernard André,Magali Lozano,Laurent Bizet,Malte C. Schroeder,Guillaume Schimmel,Michel Moret,Mark Stanley,W. A. Rison,Oliver Maurice,Bruno Esmiller,Knut Michel,Walter Haas,Thomas Metzger,Marcos Rubinstein,Farhad Rachidi,Vernon Cooray,André Mysyrowicz,Jérôme Kasparian & Jean-Pierre Wolf
Nature Photonics Published:16 January 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-022-01139-z

Abstract
Lightning discharges between charged clouds and the Earth’s surface are responsible for considerable damages and casualties. It is therefore important to develop better protection methods in addition to the traditional Franklin rod. Here we present the first demonstration that laser-induced filaments—formed in the sky by short and intense laser pulses—can guide lightning discharges over considerable distances. We believe that this experimental breakthrough will lead to progress in lightning protection and lightning physics. An experimental campaign was conducted on the Säntis mountain in north-eastern Switzerland during the summer of 2021 with a high-repetition-rate terawatt laser. The guiding of an upward negative lightning leader over a distance of 50 m was recorded by two separate high-speed cameras. The guiding of negative lightning leaders by laser filaments was corroborated in three other instances by very-high-frequency interferometric measurements, and the number of X-ray bursts detected during guided lightning events greatly increased. Although this research field has been very active for more than 20 years, this is the first field-result that experimentally demonstrates lightning guided by lasers. This work paves the way for new atmospheric applications of ultrashort lasers and represents an important step forward in the development of a laser based lightning protection for airports, launchpads or large infrastructures.