マイクロエレクトロニクスが生体ロボットの遠隔操作を可能にする Microelectronics give researchers remote control over biological robots
2023-01-18 ノースウェスタン大学
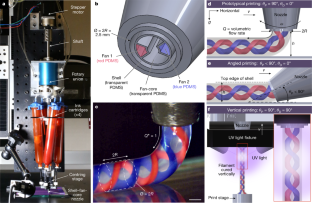
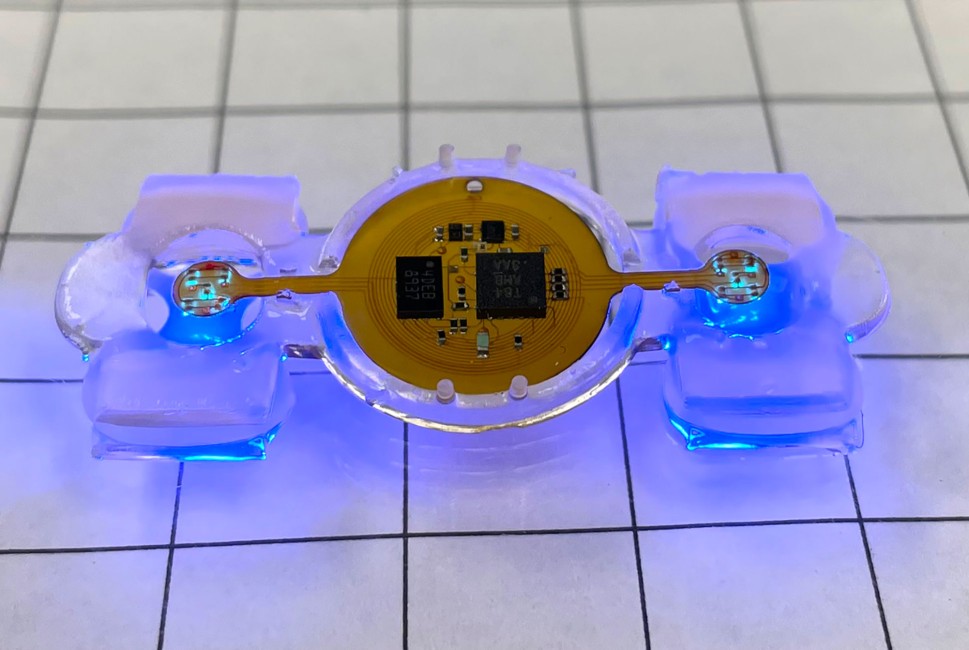 Remotely controlled miniature biological robots have many potential applications in medicine, sensing and environmental monitoring. Image courtesy of Yongdeok Kim
Remotely controlled miniature biological robots have many potential applications in medicine, sensing and environmental monitoring. Image courtesy of Yongdeok Kim
・ノースウェスタン大学とイリノイ大学アーバナ・シャンペーン校を中心とする研究者らは、このハイブリッド型「eBiobots」は、柔らかい素材、生きた筋肉、マイクロエレクトロニクスを組み合わせた最初のものである、と語った。研究者らは、このセンチメートル・スケールの生物学的機械について、学術誌『Science Robotics』に発表しました。
・Bashir教授の研究グループは、3Dプリントされた柔らかいポリマー骨格に成長したマウスの筋肉組織を動力源とする小型生物ロボット、バイオボットの開発で先駆者的な役割を果たしている。2012年に歩行型バイオボットを、2016年には光活性化型バイオボットを実証した。光による活性化により、研究者たちはある程度の制御が可能になったが、研究室以外の場所で光パルスをバイオボットに供給する方法という問題により、実用化は制限されていた。
・この問題に対する答えは、フレキシブルバイオエレクトロニクスのパイオニアであるノースウェスタン大学のジョン・A・ロジャース教授によってもたらされ、彼のチームは、小型の無線マイクロエレクトロニクスとバッテリーフリーのマイクロLEDの統合に貢献しました。これにより、研究者たちはバイオボットを遠隔操作することができるようになったのです。
・研究者らは、バイオボットの実用化に必要な自由な動きを実現するために、かさばるバッテリーや固定用のワイヤーを排除することに取り組みました。共同研究者であるヒューストン大学生体医工学部助教授のZhengwei Li氏は、「eBiobotsは、受電コイルで電力を回収し、安定した出力電圧でマイクロLEDに電力を供給しています」と述べています。
・研究者は、LEDのパルスを促す無線信号をeBiobotsに送信することができます。LEDは、光に敏感な人工筋肉を刺激して収縮させ、ポリマーの脚を動かして、機械が「歩く」ようにします。マイクロLEDは、筋肉の特定の部分を刺激して、eBiobotを希望する方向に回転させることができる。
・研究者たちは、計算機モデリングを用いて、堅牢性、速度、操縦性を高めるためにeBiobotの設計と部品の統合を最適化しました。イリノイ大学機械科学・工学部のMattia Gazzola教授が、eBiobotのシミュレーションと設計を主導しました。Gazzola教授と、Gazzola教授の研究室の共同博士研究員であるXiaotian Zhang氏は、「足場の反復設計と積層造形法による3Dプリントにより、実験と性能改善のサイクルを迅速に行うことができました」と述べています。
<関連情報>
- https://news.northwestern.edu/stories/2023/01/muscle-powered-robots-have-freedom-of-movement/
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scirobotics.add1053
電池不要のワイヤレス光電子工学を用いた筋駆動小型ロボットの遠隔制御 Remote control of muscle-driven miniature robots with battery-free wireless optoelectronics
ongdeok Kim ,Yiyuan Yang,Xiaotian Zhang,Zhengwei Li,Abraham Vázquez-Guardado,Insu Park ,Jiaojiao Wang,Andrew I. Efimov,Zhi Dou,Yue Wang ,Junehu Park ,Haiwen Luan ,Xinchen Ni,Yun Seong Kim,Janice Baek,Joshua Jaehyung Park ,Zhaoqian Xie ,Hangbo Zhao,Mattia Gazzola,John A. Rogers,Rashid Bashir
Science Robotics Published:18 Jan 2023
DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.add1053
Abstract
Bioengineering approaches that combine living cellular components with three-dimensional scaffolds to generate motion can be used to develop a new generation of miniature robots. Integrating on-board electronics and remote control in these biological machines will enable various applications across engineering, biology, and medicine. Here, we present hybrid bioelectronic robots equipped with battery-free and microinorganic light-emitting diodes for wireless control and real-time communication. Centimeter-scale walking robots were computationally designed and optimized to host on-board optoelectronics with independent stimulation of multiple optogenetic skeletal muscles, achieving remote command of walking, turning, plowing, and transport functions both at individual and collective levels. This work paves the way toward a class of biohybrid machines able to combine biological actuation and sensing with on-board computing.