この技術は、現在ISSで使われているものよりも安価で、小型・軽量です。 The technique is cheaper, smaller, and lighter than what the ISS uses today.
2022-08-15 ジョージア工科大学
宇宙で液体から気体を取り出そうとすると、他のプロセスを使う必要がある。
注射器の側面に磁石を取り付け、化学薬品やエキストラバージンオリーブオイルなどの溶液から気泡を追い出す能力をテストすることにした。
水は非常に弱い磁気を帯びている。微小重力下では、磁石は顕著な力を発揮することができる。この小規模実験の結果、使用する溶液によって気泡を磁石に引き付けたり、反発させたりできることがわかり、原理を実証することができた。
<関連情報>
- https://www.thedailybeast.com/magnets-could-lead-to-cheaper-and-easier-oxygen-production-for-astronauts-in-space
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41526-022-00212-9
微小重力下における磁気相分離 Magnetic phase separation in microgravity
Álvaro Romero-Calvo,Ömer Akay,Hanspeter Schaub & Katharina Brinkert
npj microgravity Published:08 August 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41526-022-00212-9
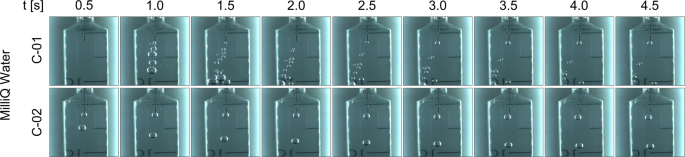
Abstract
The absence of strong buoyancy forces severely complicates the management of multiphase flows in microgravity. Different types of space systems, ranging from in-space propulsion to life support, are negatively impacted by this effect. Multiple approaches have been developed to achieve phase separation in microgravity, whereas they usually lack the robustness, efficiency, or stability that is desirable in most applications. Complementary to existing methods, the use of magnetic polarization has been recently proposed to passively induce phase separation in electrolytic cells and other two-phase flow devices. This article illustrates the dia- and paramagnetic phase separation mechanism on MilliQ water, an aqueous MnSO4 solution, lysogeny broth, and olive oil using air bubbles in a series of drop tower experiments. Expressions for the magnetic terminal bubble velocity are derived and validated and several wall–bubble and multi-bubble magnetic interactions are reported. Ultimately, the analysis demonstrates the feasibility of the dia- and paramagnetic phase separation approach, providing a key advancement for the development of future space systems.


