サンディアの研究により、持続可能なジェット燃料への道が開かれる Sandia research paves way for sustainable jet fuel
2022-04-20 サンディア国立研究所(SNL)
・ロスアラモス国立研究所の研究者と共同で、シクロアルカン(水素原子と炭素原子が単結合のみで環状に配列した分子)の物性を探った。シクロアルカンをジェット燃料に使用すると、現在の燃料に比べて凝縮痕の形成や煤煙の排出を抑えられる可能性がある。
・研究チームは、この研究成果を『Frontiers in Energy Research』誌に発表しています。
<関連情報>
- https://newsreleases.sandia.gov/aviation_emissions/
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenrg.2021.771697/full
持続可能な航空燃料への応用を目指したシクロアルカンの構造・物性相関の構築 Building Structure-Property Relationships of Cycloalkanes in Support of Their Use in Sustainable Aviation Fuels
Alexander Landera, Ray P. Bambha, Naijia Hao, Sai Puneet Desai, Cameron M. Moore, Andrew D. Sutton and Anthe George
Frontiers in Energy Research Published:31 January 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2021.771697
Abstract
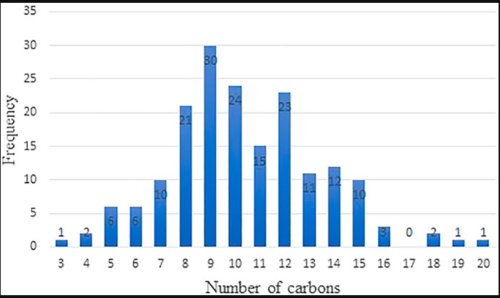
In 2018 13.7 EJ of fuel were consumed by the global commercial aviation industry. Worldwide, demand will increase into the foreseeable future. Developing Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAFs), with decreased CO2 and soot emissions, will be pivotal to the on-going mitigation efforts against global warming. Minimizing aromatics in aviation fuel is desirable because of the high propensity of aromatics to produce soot during combustion. Because aromatics cause o-rings to swell, they are important for maintaining engine seals, and must be present in at least 8 vol% under ASTM-D7566. Recently, cycloalkanes have been shown to exhibit some o-ring swelling behavior, possibly making them an attractive substitute to decrease the aromatic content of aviation fuel. Cycloalkanes must meet specifications for a number of other physical properties to be compatible with jet fuel, and these properties can vary greatly with the cycloalkane chemical structure, making their selection difficult. Building a database of structure-property relationships (SPR) for cycloalkanes greatly facilitates their furthered inclusion into aviation fuels. The work presented in this paper develops SPRs by building a data set that includes physical properties important to the aviation industry. The physical properties considered are energy density, specific energy, melting point, density, flashpoint, the Hansen solubility parameter, and the yield sooting index (YSI). Further, our data set includes cycloalkanes drawn from the following structural groups: fused cycloalkanes, n-alkylcycloalkanes, branched cycloalkanes, multiple substituted cycloalkanes, and cycloalkanes with different ring sizes. In addition, a select number of cycloalkanes are blended into Jet-A fuel (POSF-10325) at 10 and 30 wt%. Comparison of neat and blended physical properties are presented. One major finding is that ring expanded systems, those with more than six carbons, have excellent potential for inclusion in SAFs. Our data also indicate that polysubstituted cycloalkanes have higher YSI values.