2019/1/8 アメリカ合衆国デラウェア大学 (UD)
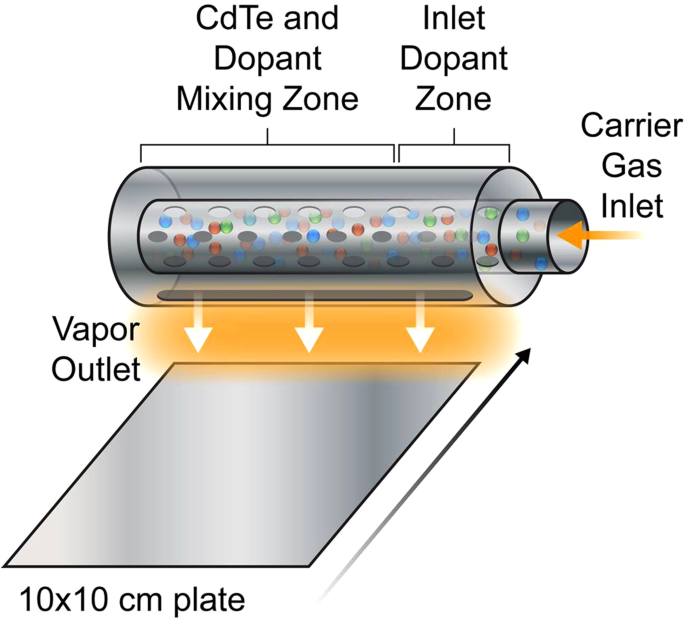
・ UD が、薄膜太陽電池のエネルギー変換効率向上とコスト低減を可能にする、新しい蒸気搬送蒸着 (vapor transport deposition: VTD)システム(特許取得済)を開発。
・ シリコンウェハーに比して太陽電池市場にて小規模でも占有率が増大している薄膜技術は、フレキシブルで軽量な太陽光パネルの迅速な製造や設計とアプリケーションの幅広い選択肢といった利点を提供。2016 年にはエネルギー変換効率 22.1%を達成している。
・ 太陽電池の薄膜材料は、熱と圧力によるプロセスで基板上に成長させて積層した、平方インチ当たり数百万個の結晶から構成される。このような結晶成長時の各結晶粒子の特性の調整が重要となる。
・ 新 VDT システムでは、薄膜成長時、太陽電池性能を向上させる特性が制御可能な温度にて追加的な元素を微量添加(ドーピング)する。これにより導電性が向上して太陽電池の電圧が増加する。・ 今回は代表的なテルル化カドミウム(CdTe)薄膜材料を使用し、アンチモン(Sb)、ヒ素(As)およびリン (P)による各ドーピングシナリオを試験した結果、全ドーパントが優れた特性を付加して高いドーピングレベルを示したが、特にヒ素とアンチモンで顕著であった。
・ 同 VDT システムでは、薄膜成長時の熱力学的な制限にも対処。CdTe 格子でテルル原子 1 個を除去し、いずれかのドーパントを挿入して電子を失った状態は熱力学的に維持不可能だが、CdTe 格子の急速成長・冷却により正孔を獲得することで導電性が向上。
・ これまで困難とされてきた CdTe 薄膜の高いドーピングを今回実証し、1V 超の電圧と 25%のエネルギー変換効率の実現の見込みが得られた。今後は電子の流れの向上や、ドーパント量を低減した同等の効果獲得を目指す。
・ 米国立再生可能エネルギー研究所(NREL)が、同薄膜による高性能太陽電池製造方法を開発。UD による同薄膜の測定値を認証し、同研究所にて同 VDT システムを再現した。
URL: https://www.udel.edu/udaily/2019/january/solar-energy-renewable-photovoltaics-thin-film/
(関連情報)
Scientific Reports 掲載論文(フルテキスト)
Overcoming Carrier Concentration Limits in Polycrystalline CdTe Thin Films with In Situ Doping
URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-32746-y
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
Abstract
Thin film materials for photovoltaics such as cadmium telluride (CdTe), copper-indium diselenide-based chalcopyrites (CIGS), and lead iodide-based perovskites offer the potential of lower solar module capital costs and improved performance to microcrystalline silicon. However, for decades understanding and controlling hole and electron concentration in these polycrystalline films has been extremely challenging and limiting. Ionic bonding between constituent atoms often leads to tenacious intrinsic compensating defect chemistries that are difficult to control. Device modeling indicates that increasing CdTe hole density while retaining carrier lifetimes of several nanoseconds can increase solar cell efficiency to 25%. This paper describes in-situ Sb, As, and P doping and post-growth annealing that increases hole density from historic 1014 limits to 1016–1017 cm−3 levels without compromising lifetime in thin polycrystalline CdTe films, which opens paths to advance solar performance and achieve costs below conventional electricity sources.