エキゾチックな2次元物質の交互積層が、平衡状態にある磁石の構造体に「エントロピー駆動型秩序」を生み出す Interactions between alternating layers of exotic, 2D material create ‘entropy-driven order’ in a structured system of magnets at equilibrium
2022-04-08 アメリカ・ロスアラモス国立研究所(LANL)
・ロスアラモスの物理学者で、この研究に関する論文をNature Physicsに発表したクリスティアーノ・ニソリは、「逆説的ですが、システムはより無秩序になりたがっているから秩序化するのです」と述べている。Nature Physics誌に掲載された研究論文の共著者であるクリスティアーノ・ニソーリは「我々の研究は、平衡状態にある磁石の構造システムにおけるエントロピー駆動型の秩序を示しています。」
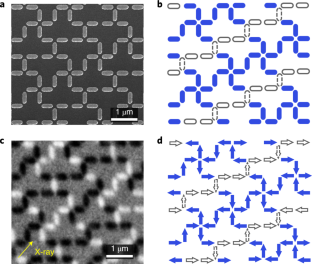
・テトリス・スピンアイスは、相互作用しながらもフラストレーションのある非常に小さな磁石の2次元配列で構成されており、この2つのケースが混在する不思議な物質である。磁極の向きがフラストレーションになっているため、秩序を保ちながら無秩序な状態になっている。低温では、秩序と無秩序が交互に繰り返される縞模様に分解される。
・秩序が増加するとエントロピーが増加するという明らかなパラドックスは、交互に並ぶ層間のエントロピー的相互作用によって解決される。秩序化された縞模様の相互作用によって、システムは他の縞模様の無秩序を増加させるのである。このように、秩序はエネルギーの減少を伴わずに、エントロピーの増加によって起こるのである。
<関連情報>
ナノ磁性体アレイのエントロピー駆動型秩序 Entropy-driven order in an array of nanomagnets
Hilal Saglam,Ayhan Duzgun,Aikaterini Kargioti,Nikhil Harle,Xiaoyu Zhang,Nicholas S. Bingham,Yuyang Lao,Ian Gilbert,Joseph Sklenar,Justin D. Watts,Justin Ramberger,Daniel Bromley,Rajesh V. Chopdekar,Liam O’Brien,Chris Leighton,Cristiano Nisoli &Peter Schiffer
Nature Physics Published: 07 April 2022
Abstract
Long-range ordering is typically associated with a decrease in entropy. Yet, it can also be driven by increasing entropy in certain special cases. Here we demonstrate that artificial spin-ice arrays of single-domain nanomagnets can be designed to produce such entropy-driven order. We focus on the tetris artificial spin-ice structure, a highly frustrated array geometry with a zero-point Pauling entropy, which is formed by selectively creating regular vacancies on the canonical square ice lattice. We probe thermally active tetris artificial spin ice both experimentally and through simulations, measuring the magnetic moments of the individual nanomagnets. We find two-dimensional magnetic ordering in one subset of these moments, which we demonstrate to be induced by disorder (that is, increased entropy) in another subset of the moments. In contrast with other entropy-driven systems, the discrete degrees of freedom in tetris artificial spin ice are binary and are both designable and directly observable at the microscale, and the entropy of the system is precisely calculable in simulations. This example, in which the system’s interactions and ground-state entropy are well defined, expands the experimental landscape for the study of entropy-driven ordering.