2025-11-28 東京科学大学
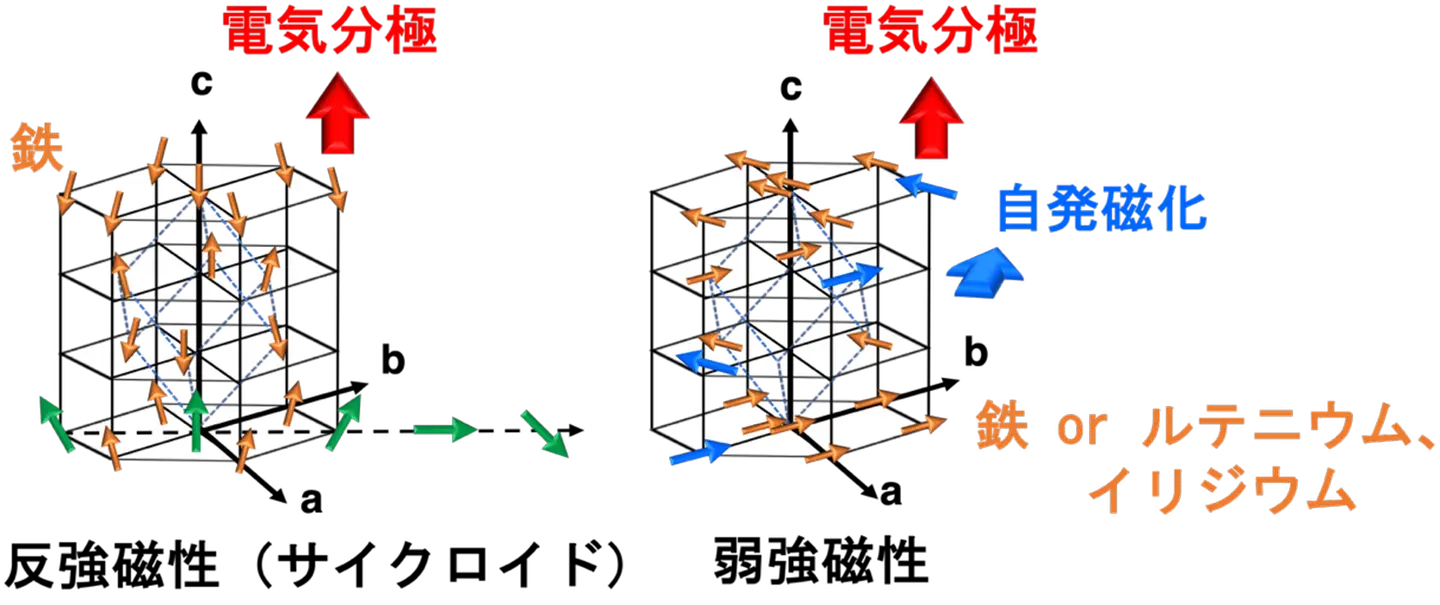
図1. 鉄酸ビスマス(左)と、A-Bサイト元素置換鉄酸ビスマス(右)の磁気構造の模式図。鉄酸ビスマスでは右に進むにつれてスピンの方向が一回転するサイクロイド変調があるため、スピンの磁化は打ち消し合い自発磁化は現れない。一方、元素置換鉄酸ビスマスではスピンが傾斜しているため、磁化は打ち消し合わずに電気分極に直交した自発磁化が現れる。
<関連情報>
AサイトおよびBサイト置換ビスマスフェライトにおける傾斜スピン弱強磁性と負の熱膨張の実現 Achieving Canted-Spin Weak Ferromagnetism and Negative Thermal Expansion in A- and B-Site-Substituted Bismuth Ferrite
Kano Hatayama,Jun Miyake,Daiki Ono,Yusuke Shiono,Takumi Nishikubo,Koomok Lee,Shogo Wakazaki,Hena Das,Kei Shigematsu,Tomoko Onoue,Ko Mibu,Shogo Kawaguchi,Takafumi Yamamoto,and Masaki Azuma
Journal of the American Chemical Society Published: November 28, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5c12255
Abstract
BiFeO3 is the most intensively investigated multiferroic material. It has a cycloidal spin modulation superimposed on G-type antiferromagnetic ordering of Fe3+ (S = 5/2), which prohibits the appearance of a net magnetization. We found that the simultaneous substitution of Ru4+ or Ir4+ for Fe3+ and Ca2+ for Bi3+ suppressed the cycloidal modulation and induced canted weak ferromagnetism at room temperature, while preserving the polar rhombohedral crystal structure. Moreover, the A- and B-site substitutions substantially lowered the ferroelectric transition temperature and resulted in a 1.77% volumetric negative thermal expansion around room temperature. These findings open an avenue for designing new BiFeO3-based functional materials.