2025-08-14 テキサス A&M大学
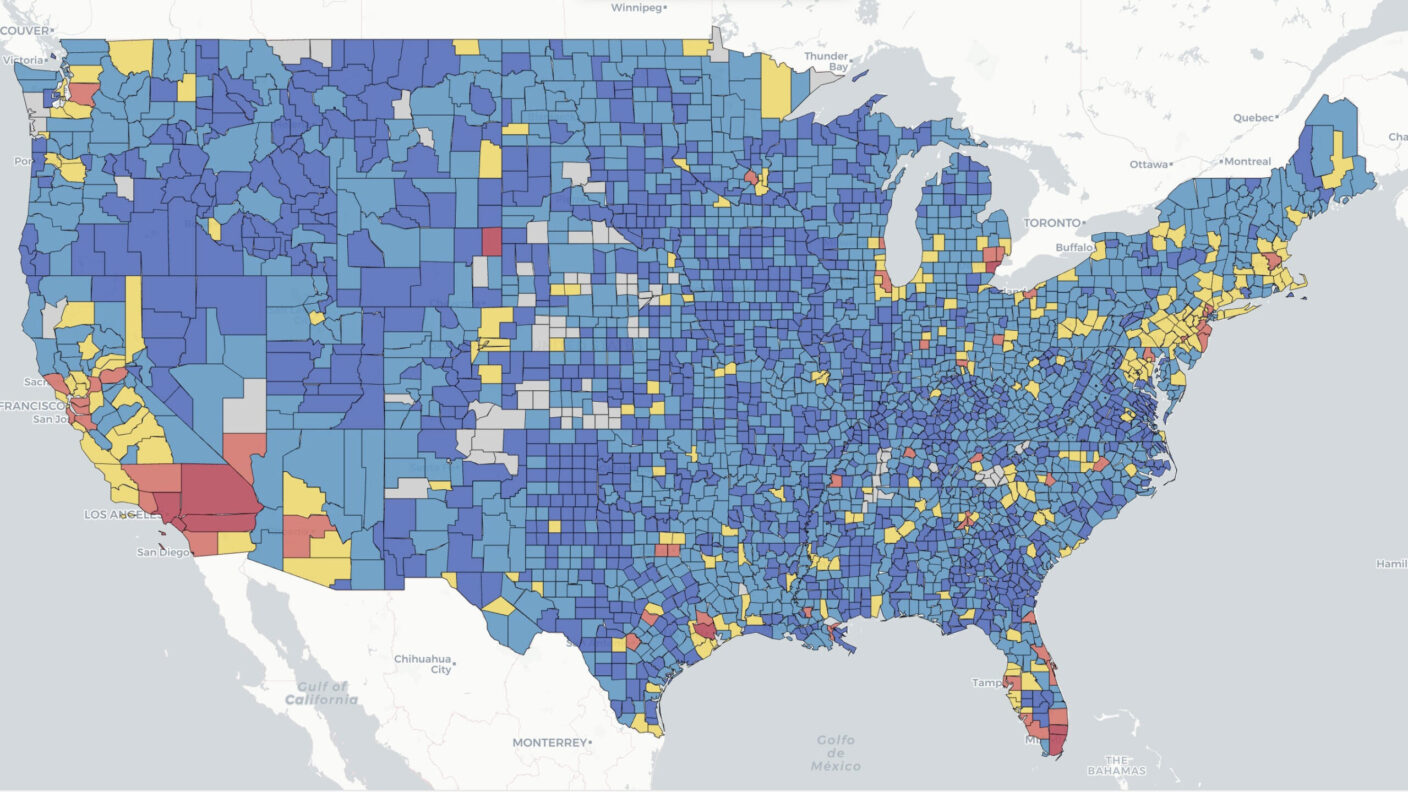
Researchers at Texas A&M University have created a Nationwide Power System Vulnerability Index that assigns individual counties a rating based on their likelihood of being affected by power outages.
Credit: Urban Resilience AI Lab
<関連情報>
- https://stories.tamu.edu/news/2025/08/14/texas-am-researchers-map-americas-power-outage-hot-spots-using-ai/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0306261925010906?via%3Dihub
全米の郡を対象に解釈可能な機械学習を用いて電力システム脆弱性指数を確立 Establishing nationwide power system vulnerability index across US counties using interpretable machine learning
Junwei Ma, Bo Li, Olufemi A. Omitaomu, Ali Mostafavi
Applied Energy Available online: 30 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2025.126360
Highlights
- A nationwide Power System Vulnerability Index (PSVI) has been developed for 3022 U.S. counties over the past decade.
- The PSVI reveals a steady rise in power system vulnerability across the U.S. from 2014 to 2023.
- Regions including the West Coast, East Coast, Gulf of Mexico, and the Great Lakes megalopolis demonstrate notably high levels of vulnerability.
- The influence of urban form and strcuture on power system vulnerability has been recognized as a key factor.
Abstract
Power outages have become increasingly frequent, intense, and prolonged in the US due to climate change, aging electrical grids, and rising energy demand. However, largely due to the absence of granular spatiotemporal outage data, we lack data-driven evidence and analytics-based metrics to quantify power system vulnerability. This limitation has hindered the ability to effectively evaluate and address vulnerability to power outages in US communities. Here, we collected ∼179 million power outage records at 15-min intervals across 3022 US contiguous counties (96.15 % of the area) from 2014 to 2023. We developed a power system vulnerability assessment framework based on three dimensions (intensity, frequency, and duration) and applied interpretable machine learning models (XGBoost and SHAP) to compute Power System Vulnerability Index (PSVI) at the county level. Our analysis reveals a consistent increase in power system vulnerability across the US counties over the past decade. We identified 318 counties across 45 states as hotspots for high power system vulnerability, particularly in the West Coast (California and Washington), the East Coast (Florida and the Northeast area), the Great Lakes megalopolis (Chicago-Detroit metropolitan areas), and the Gulf of Mexico (Texas). Our heterogeneity analysis indicates that urban counties and those located along regional transmission boundaries tend to exhibit significantly higher vulnerability. Our results highlight the significance of the proposed PSVI for evaluating the vulnerability of communities to power outages. The findings underscore the widespread and pervasive impact of power outages across the country and offer crucial insights to support infrastructure operators, policymakers, and emergency managers in formulating policies and programs aimed at enhancing the resilience of the US power infrastructure.