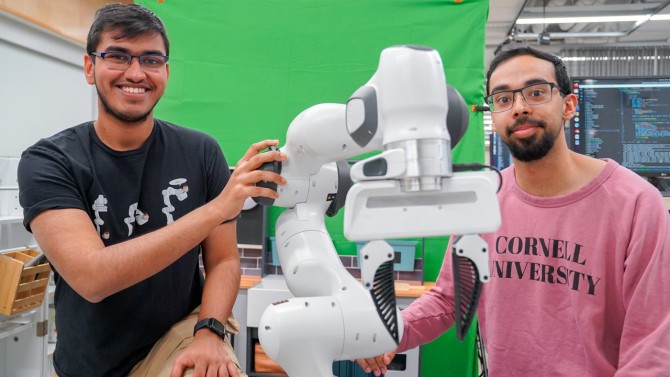
2025-04-22 アメリカ合衆国・コーネル大学
<関連情報>
- https://news.cornell.edu/stories/2025/04/robot-see-robot-do-system-learns-after-watching-how-tos
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/2409.06615
実行不一致下でのワンショット模倣 One-Shot Imitation under Mismatched Execution
Kushal Kedia, Prithwish Dan, Angela Chao, Maximus Adrian Pace, Sanjiban Choudhury
arXiv:2409.06615v6 28 Mar 2025
Abstract
Human demonstrations as prompts are a powerful way to program robots to do long-horizon manipulation tasks. However, translating these demonstrations into robotexecutable actions presents significant challenges due to execution mismatches in movement styles and physical capabilities. Existing methods for human-robot translation either depend on paired data, which is infeasible to scale, or rely heavily on frame-level visual similarities that often break down in practice. To address these challenges, we propose RHyME, a novel framework that automatically pairs human and robot trajectories using sequence-level optimal transport cost functions. Given longhorizon robot demonstrations, RHyME synthesizes semantically equivalent human videos by retrieving and composing shorthorizon human clips. This approach facilitates effective policy training without the need for paired data. RHyME successfully imitates a range of cross-embodiment demonstrators, both in simulation and with a real human hand, achieving over 50% increase in task success compared to previous methods. We release our code and datasets at this website.