2023-10-16 ジョージア工科大学
◆この技術の初期段階での原油成分の分離は、世界全体で使用されているエネルギーの約1%に相当し、ポリマー膜分離技術はバイオ燃料、生分解性プラスチック、パルプ、紙製品などさまざまな用途に応用できます。
◆ジョージア工科大学の研究チームは、このポリマー膜だけでなく、新しいポリマー膜の性能を予測するための人工知能ツールも開発しており、今後の開発を加速させる役割を果たすことが期待されています。この研究成果は2023年10月16日に「ネイチャー・マテリアルズ」誌に発表されました。
<関連情報>
- https://research.gatech.edu/new-polymer-membranes-ai-predictions-could-dramatically-reduce-energy-water-use-oil-refining
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41563-023-01682-2
膜ベースの炭化水素分離のためのスピロ環モノマーからの溶液処理可能なポリトリアゾール Solution-processable polytriazoles from spirocyclic monomers for membrane-based hydrocarbon separations
Nicholas C. Bruno,Ronita Mathias,Young Joo Lee,Guanghui Zhu,Yun-Ho Ahn,Neel D. Rangnekar,J. R. Johnson,Scott Hoy,Irene Bechis,Andrew Tarzia,Kim E. Jelfs,Benjamin A. McCool,Ryan Lively & M. G. Finn
Nature Materials Published:16 October 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-023-01682-2
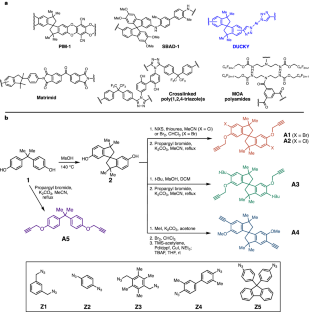
Abstract
The thermal distillation of crude oil mixtures is an energy-intensive process, accounting for nearly 1% of global energy consumption. Membrane-based separations are an appealing alternative or tandem process to distillation due to intrinsic energy efficiency advantages. We developed a family of spirocyclic polytriazoles from structurally diverse monomers for membrane applications. The resulting polymers were prepared by a convenient step-growth method using copper-catalysed azide–alkyne cycloaddition, providing very fast reaction rates, high molecular weights and solubilities in common organic solvents and non-interconnected microporosity. Fractionation of whole Arabian light crude oil and atmospheric tower bottom feeds using these materials enriched the low-boiling-point components and removed trace heteroatom and metal impurities (comparable performance with the lighter feed as the commercial polyimide, Matrimid), demonstrating opportunities to reduce the energy cost of crude oil distillation with tandem membrane processes. Membrane-based molecular separation under these demanding conditions is made possible by high thermal stability and a moderate level of dynamic chain mobility, leading to transient interconnections between micropores, as revealed by the calculations of static and swollen pore structures.



