2024-03-21 カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校(UCSD)
<関連情報>
- https://today.ucsd.edu/story/biodegradable-microplastics
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-56492-6
バイオベースの熱可塑性ポリウレタンから生成されたマイクロプラスチックの迅速な生分解 Rapid biodegradation of microplastics generated from bio-based thermoplastic polyurethane
Marco N. Allemann,Marissa Tessman,Jaysen Reindel,Gordon B. Scofield,Payton Evans,Robert S. Pomeroy,Michael D. Burkart,Stephen P. Mayfield & Ryan Simkovsky
Scientific Reports Published:12 March 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-56492-6
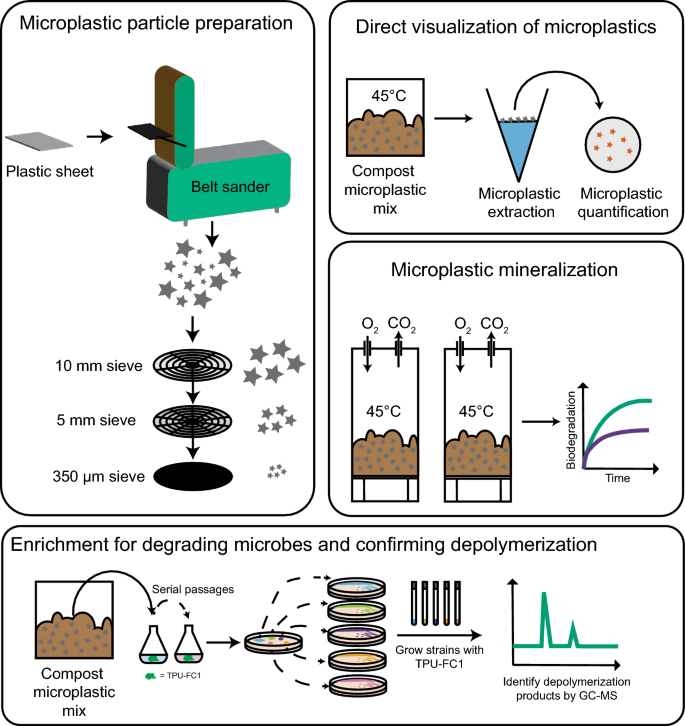
Abstract
The accumulation of microplastics in various ecosystems has now been well documented and recent evidence suggests detrimental effects on various biological processes due to this pollution. Accumulation of microplastics in the natural environment is ultimately due to the chemical nature of widely used petroleum-based plastic polymers, which typically are inaccessible to biological processing. One way to mitigate this crisis is adoption of plastics that biodegrade if released into natural environments. In this work, we generated microplastic particles from a bio-based, biodegradable thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU-FC1) and demonstrated their rapid biodegradation via direct visualization and respirometry. Furthermore, we isolated multiple bacterial strains capable of using TPU-FC1 as a sole carbon source and characterized their depolymerization products. To visualize biodegradation of TPU materials as real-world products, we generated TPU-coated cotton fabric and an injection molded phone case and documented biodegradation by direct visualization and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), both of which indicated clear structural degradation of these materials and significant biofilm formation.



