2023-07-25 韓国基礎科学研究院(IBS)
◆GOBIは従来の手法よりも精度が高く、分子から人口までのさまざまなネットワークで因果関係を推論できます。また、直接的な因果関係と間接的な因果関係を区別できるため、ノイズのあるデータでも信頼性があります。GOBIは生物学や生態学、流行病学など、多くの分野で新たな洞察をもたらすことが期待されています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.ibs.re.kr/cop/bbs/BBSMSTR_000000000738/selectBoardArticle.do
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-39983-4
一般的なモデルに基づく因果推論手法が同期の呪いと間接効果を克服する A general model-based causal inference method overcomes the curse of synchrony and indirect effect
Se Ho Park,Seokmin Ha & Jae Kyoung Kim
Nature Communications Published:24 July 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-39983-4
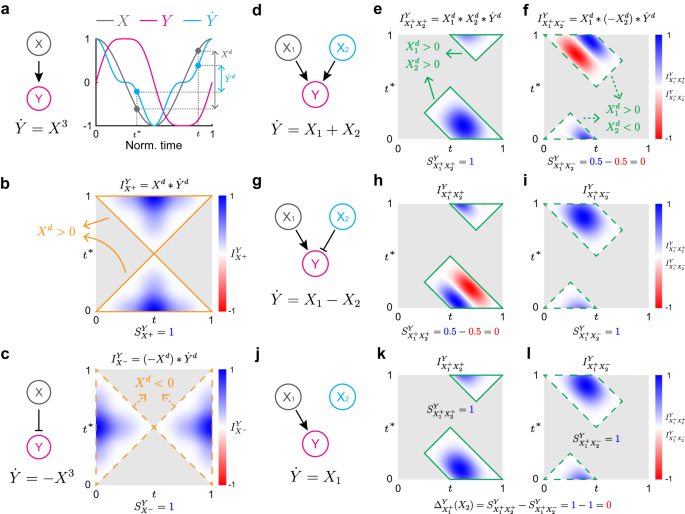
Abstract
To identify causation, model-free inference methods, such as Granger Causality, have been widely used due to their flexibility. However, they have difficulty distinguishing synchrony and indirect effects from direct causation, leading to false predictions. To overcome this, model-based inference methods that test the reproducibility of data with a specific mechanistic model to infer causality were developed. However, they can only be applied to systems described by a specific model, greatly limiting their applicability. Here, we address this limitation by deriving an easily testable condition for a general monotonic ODE model to reproduce time-series data. We built a user-friendly computational package, General ODE-Based Inference (GOBI), which is applicable to nearly any monotonic system with positive and negative regulations described by ODE. GOBI successfully inferred positive and negative regulations in various networks at both the molecular and population levels, unlike existing model-free methods. Thus, this accurate and broadly applicable inference method is a powerful tool for understanding complex dynamical systems.