EPFLの研究者は、ハーバード大学およびチューリッヒ工科大学の研究者と共同で、レーザービームに接続すると、細かく調整可能なテラヘルツ波が発生する新しい薄膜回路を開発しました。このデバイスは、光学および電気通信の分野での応用の可能性を広げるものです。 EPFL researchers have collaborated with those at Harvard and ETH Zurich on a new thin-film circuit that, when connected to a laser beam, produces finely tailorable terahertz-frequency waves. The device opens up a world of potential applications in optics and telecommunications.
2023-01-12 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
HYLABの研究者とチューリッヒ工科大学およびハーバード大学の研究者らは、ニオブ酸リチウム製のフォトニック回路を集積した極薄チップにより、テラヘルツ波の発生だけでなく、その周波数、波長、振幅、位相をカスタムメイドするソリューションを開発することに成功した。このようにテラヘルツ波を精密に制御することで、電子・光学の両分野で次世代アプリケーションに活用できる可能性がある。この成果は、『Nature Communications』誌に掲載されました。
Benea-Chelmus教授によると、研究室でテラヘルツ波を発生させたことはあるが、これまでのアプローチは、適切な周波数を発生させるために、主にバルク結晶に依存していたという。ハーバード大学の共同研究者がナノメートル単位で精密にエッチングしたニオブ酸リチウム回路を使用することで、この新しいアプローチはより効率的なものになりました。また、シリコン基板を使用することで、電子システムや光学システムへの組み込みにも適している。
「非常に高い周波数の波を発生させることは非常に困難であり、ユニークなパターンで波を発生させることができる技術は非常に限られています。私たちは今、テラヘルツ波の正確な時間形状を設計することができます。つまり、本質的に『このような波形が欲しい』と言えるのです」と彼女は説明する。
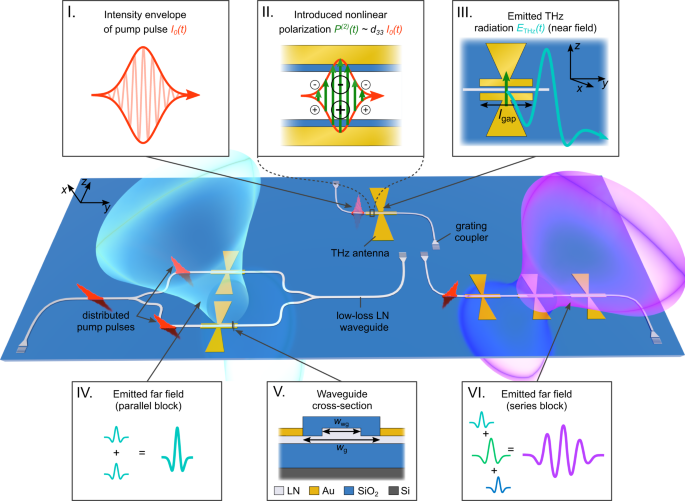
これを実現するために、Benea-Chelmus教授の研究室では、チップに導波路と呼ばれるチャネルを配置し、そこから光ファイバーから光で発生したテラヘルツ波を流す微小なアンテナを設計した。
光学の世界では、ニオブ酸リチウムの小型チップは、分光学や画像処理に特に可能性があるとBenea-Chelmusは考えている。テラヘルツ波は、非電離であることに加え、現在、骨や油絵など物質の組成を知るために使われているX線など他の多くの種類の波よりもはるかに低エネルギーである。ニオブ酸リチウムチップのようなコンパクトで非破壊的な装置は、現在の分光法に代わる、より低侵襲な方法となり得る。
次にBenea-Chelmusは、チップの導波管とアンテナの特性を微調整し、より大きな振幅と、より細かく調整された周波数と減衰率の波形を設計することに注力する予定である。また、研究室で開発されたテラヘルツ技術は、量子力学への応用にも役立つと考えている。
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/integrated-photonic-circuits-could-help-close-the-/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-35517-6
薄膜ニオブ酸リチウム集積化プラットフォームにおけるテラヘルツ波形の合成 Terahertz waveform synthesis in integrated thin-film lithium niobate platform
Alexa Herter,Amirhassan Shams-Ansari,Francesca Fabiana Settembrini,Hana K. Warner,Jérôme Faist,Marko Lončar & Ileana-Cristina Benea-Chelmus
Nature Communications Published:04 January 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-35517-6
Abstract
Bridging the “terahertz gap“ relies upon synthesizing arbitrary waveforms in the terahertz domain enabling applications that require both narrow band sources for sensing and few-cycle drives for classical and quantum objects. However, realization of custom-tailored waveforms needed for these applications is currently hindered due to limited flexibility for optical rectification of femtosecond pulses in bulk crystals. Here, we experimentally demonstrate that thin-film lithium niobate circuits provide a versatile solution for such waveform synthesis by combining the merits of complex integrated architectures, low-loss distribution of pump pulses on-chip, and an efficient optical rectification. Our distributed pulse phase-matching scheme grants shaping the temporal, spectral, phase, amplitude, and farfield characteristics of the emitted terahertz field through designer on-chip components. This strictly circumvents prior limitations caused by the phase-delay mismatch in conventional systems and relaxes the requirement for cumbersome spectral pre-engineering of the pumping light. We propose a toolbox of basic blocks that produce broadband emission up to 680 GHz and far-field amplitudes of a few V m−1 with adaptable phase and coherence properties by using near-infrared pump pulse energies below 100 pJ.