2022-04-14 ローレンス・リバモア国立研究所(LLNL)
急激な排出削減は直ちに地球の気候変動に影響を与えますが、内部変動によるノイズのために、これまでは測定結果の検証に最大20年かかると言われていました。新しい気候変動フィルタは、この時間を半分に短縮してくれます。
<関連情報>
- https://www.llnl.gov/news/speeding-detection-climate-change-response-emission-reductions
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-29247-y
年変動フィルターによる緩和のための温度応答の早期出現 Earlier emergence of a temperature response to mitigation by filtering annual variability
B. H. Samset,C. Zhou,J. S. Fuglestvedt,M. T. Lund,J. Marotzke &M. D. Zelinka
Nature Communications Published: 24 March 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29247-y
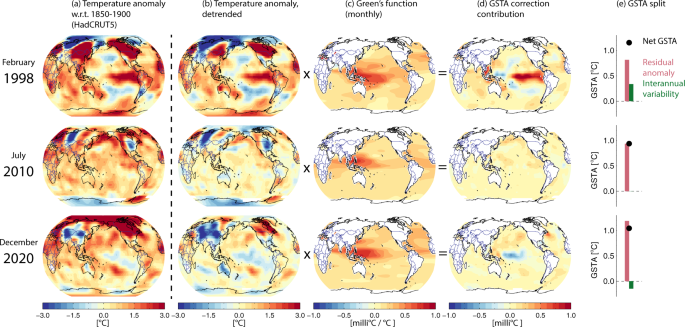
図1: 海面水温のパターンから地球表面温度偏差(GSTA)の変調を計算(3ヶ月分)。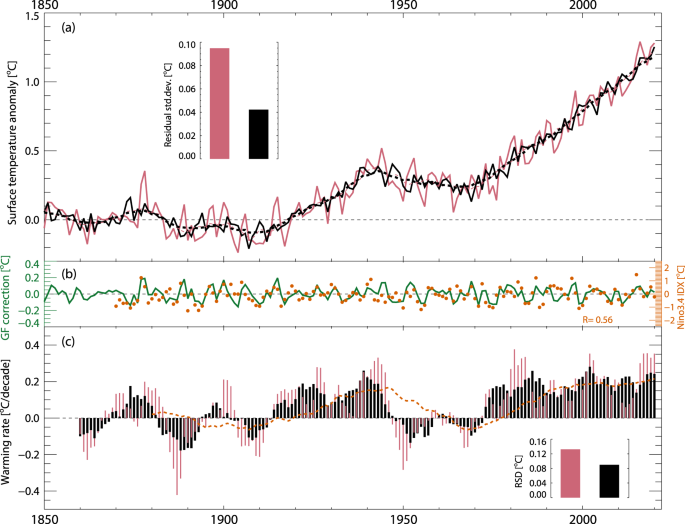
図2: HadCRUT5による全球年平均気温偏差に対するグリーン関数に基づくフィルタリングの効果。
Abstract
The rate of global surface warming is crucial for tracking progress towards global climate targets, but is strongly influenced by interannual-to-decadal variability, which precludes rapid detection of the temperature response to emission mitigation. Here we use a physics based Green’s function approach to filter out modulations to global mean surface temperature from sea-surface temperature (SST) patterns, and show that it results in an earlier emergence of a response to strong emissions mitigation. For observed temperatures, we find a filtered 2011–2020 surface warming rate of 0.24 °C per decade, consistent with long-term trends. Unfiltered observations show 0.35 °C per decade, partly due to the El Nino of 2015–2016. Pattern filtered warming rates can become a strong tool for the climate community to inform policy makers and stakeholder communities about the ongoing and expected climate responses to emission reductions, provided an effort is made to improve and validate standardized Green’s functions.


