2021-11-16 アメリカ合衆国・カリフォルニア大学校アーバイン校(UCI)
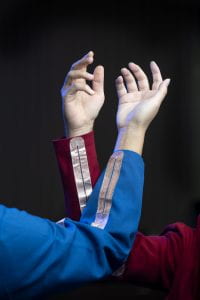
・ UCI が、衣類と近隣のデバイス間のバッテリーフリー通信によるボディ・エリア・ネットワークを実現する、フレキシブルなテキスタイルに先進的なメタ材料を統合したシステムを開発。
・ 近距離無線通信(NFC)の原理で作動しながら、その通信距離を大幅に拡張。シングルタッチ、ハイタッチ、握手や袖をさっと動かすことで、近くにある電子デイバイスとデジタルに相互作用し、安全な支払い、エネルギーや情報の交換や自動車ドアの解錠を可能にする。別の衣類を通信に簡単に取り入れることもできる。
・ バッテリーフリーのセンサーのワイヤレス充電・給電等のアプリケーションを発展させた NFC プロトコルでは、その通信範囲が数インチに限られることが難点。新システムは、銅とアルミニウムのエッチドフォイルをベースとした受動磁気メタ材料を利用することで、信号到達範囲を 4 インチ(約 10cm)超に拡張した。
・ スマートファブリックの最新技術であるワイヤ接続とは異なり、新システムでは磁気誘導を通じて信号を送るため、脚の動きを測定するパンツが心拍等を追跡するシャツと通信するアスリート・ギアのような、複数衣類間の同調が可能となる。
・ 新メタ材料を搭載した病衣にセンサーを統合すれば、、医療スタッフによる多数の患者へのセンサーの取り付け作業を不要にする等、医療用アプリケーションは無数にある。新メタ材料は低コスト、製造が容易、カスタマイズ可能で、既製の衣類に熱プレスで装着できる。
・ 本研究は、米国立科学財団(NSF)が支援した。
URL: https://news.uci.edu/2021/11/16/uci-invention-lets-people-pay-for-purchases-with-a-high-five/
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
(関連情報)
Nature Electronics 掲載論文(アブストラクトのみ:全文は有料)
Textile-integrated metamaterials for near-field multibody area networks
URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-021-00663-0
Abstract
Wearable and implantable sensors can be linked together to create multi-node wireless networks that could be of use in the development of advanced healthcare monitoring technologies. Such body area networks require secure, seamless and versatile communication links that can operate across the complex human body, but they typically suffer from short ranges, low power or the need for direct-connection terminals. Here we show that textile-integrated metamaterials can be used to drive long-distance near-field communication (NFC)-based magneto-inductive waves along and between multiple objects. The metamaterials are built from arrays of discrete, anisotropic magneto-inductive elements, creating a mechanically flexible system capable of battery-free communication among NFC-enabled devices that are placed anywhere close to the network. Our approach offers a secure and on-demand body area network that has the potential for straightforward expansion and can span across different pieces of clothing, objects and people.