(‘Soft Tactile Logic’ Tech Distributes Decision-Making Throughout Stretchable Material)
2019/9/13 アメリカ合衆国ノースカロライナ大学
・ ノースカロライナ大学は、タコから着想を得て、中央処理型ではなく感知、計算、応答ができ、ロボットでもコンピューターでもない両方の特性を備えたデバイスを開発。新技術は、ソフトロボットから人工装具まで、様々なアプリケーションに適用可能。
・ 研究者らは、同デバイスを、「ソフトなタクタイルロジック(soft tactile logic)」と呼び、様々な種類のプロトタイプを開発。従来の中央処理型の半導体ベースのロジックシステムとは異なり、センサーが入力情報を受信する材料レベルで判断処理する機能を実証。
・ タコは中央に脳があるが、各足にもそれぞれ神経系がある分散型。このことからヒントを得て、脳からの中央指令型ではなく、各足のセンサーが受信する情報から「判断する」手法を考えた。
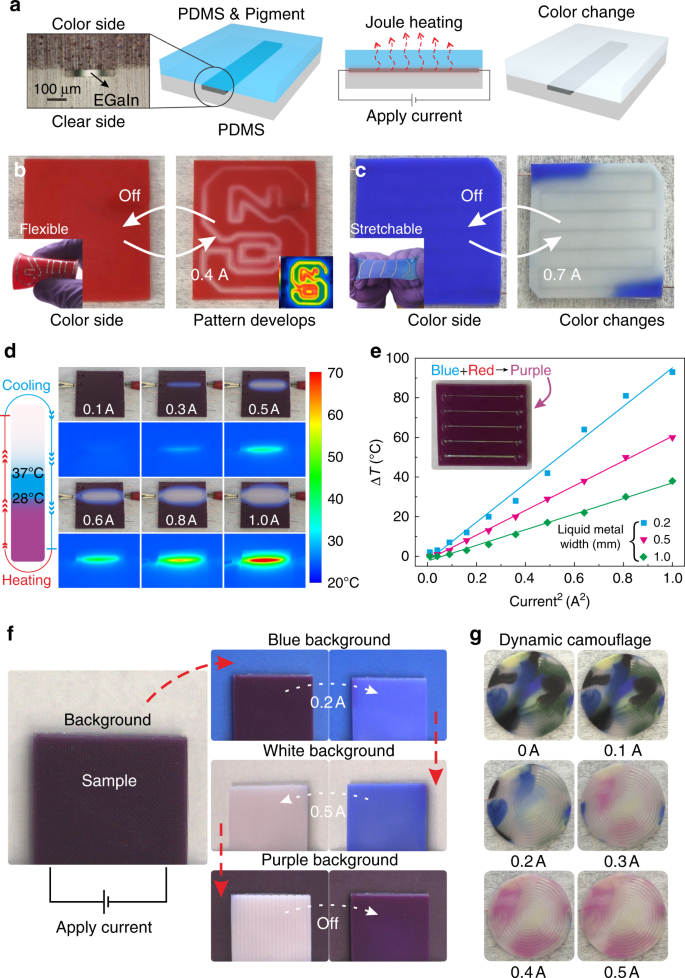
・ ソフトなタクタイルロジックのプロトタイプのコアの構造は共通で、ソフトでストレッチャブルなシリコン形状に混ぜこまれた、温度差で変色する色素。着色されたシリコンには、室温で液体の金属で満たされたチャンネルがあり、柔らかくフレキシブルなワイヤー状の神経系を効果的に形成。
・ シリコンを押したり引き伸ばしたりすると、液体状の金属が変形し、電気抵抗が増し、電気が通ると温度が上昇。高温になると周囲の温度感受性色素の色が変化。構造全体が、タッチと歪みの感知で調整可能。
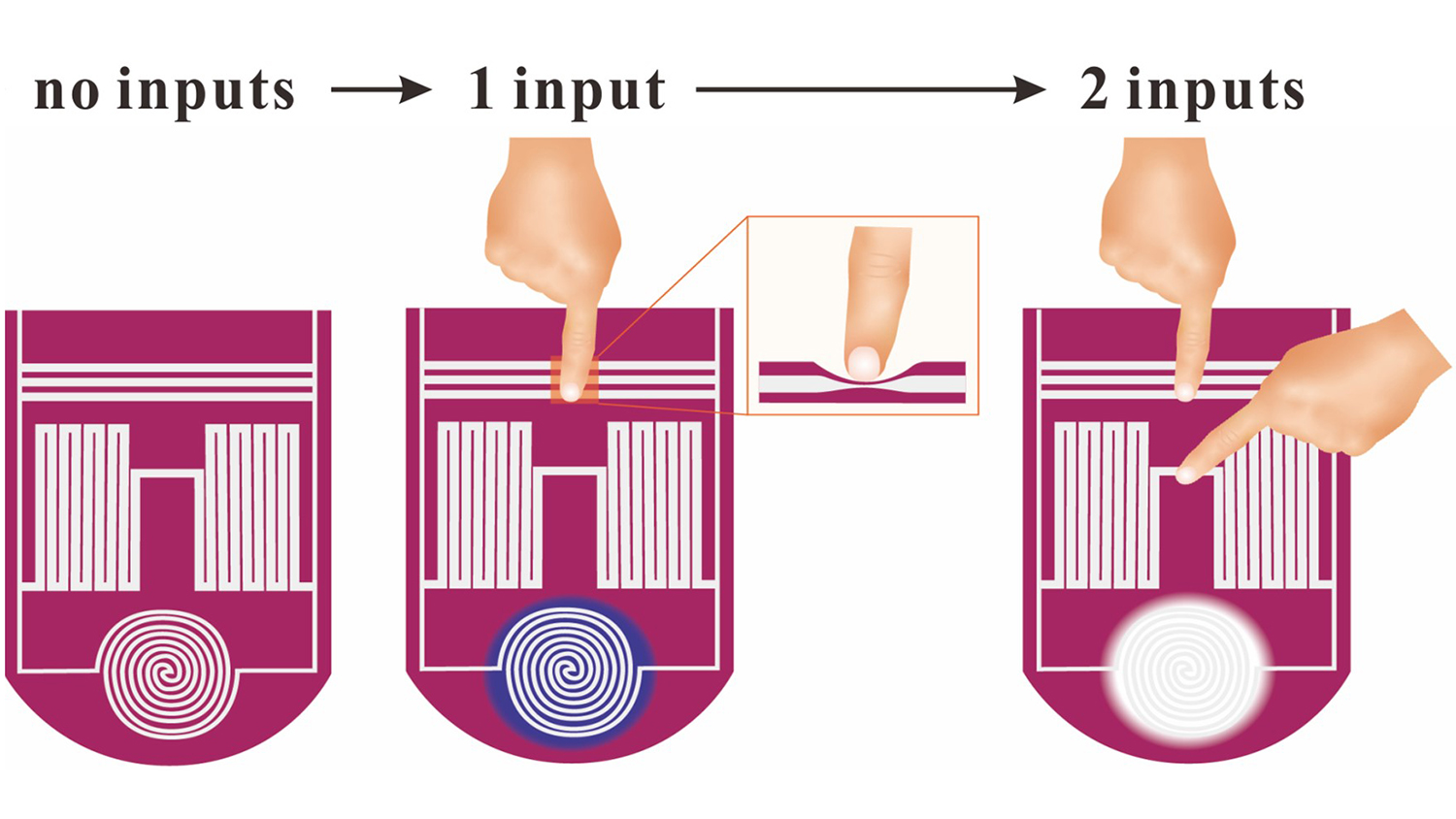
・ 研究者らはまた、タッチして液体金属を変形させてネットワークの他の場所に電気エネルギーを再分配し、材料を変色させ、モーターを駆動し、点灯する、ソフトなタクタイルロジックのプロトタイプを開発。シリコンの一か所に触れるのと、二か所に触れるのとでは異なる反応が生じ、タッチに応じたシンプルなロジックが施行。
・ 本研究は、ソフトな材料に意思決定を構築する新しい概念を実証したもの。生物の中央処理型ではない意思決定のパラダイムを模倣することで、完全にソフトな材料を使用して、材料ベースの分散型ロジックが可能であることを提示。
・ 研究者らは現在、バイオロジカルなシステムを活用したセンサーやアクチュエーターに着想を得た、より複雑で柔軟な回路を作製しようと探求中。
URL: https://news.ncsu.edu/2019/09/soft-tactile-logic/
(関連情報)
Nature Communications 掲載論文(フルテキスト) Materials tactile logic via innervated soft thermochromic elastomers
URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-019-12161-1
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
Abstract
Conventional machines rely on rigid, centralized electronic components to make decisions, which limits complexity and scaling. Here, we show that decision making can be realized on the material-level without relying on semiconductor-based logic. Inspired by the distributed decision making that exists in the arms of an octopus, we present a completely soft, stretchable silicone composite doped with thermochromic pigments and innervated with liquid metal. The ability to deform the liquid metal couples geometric changes to Joule heating, thus enabling tunable thermo-mechanochromic sensing of touch and strain. In more complex circuits, deformation of the metal can redistribute electrical energy to distal portions of the network in a way that converts analog tactile ‘inputs’ into digital colorimetric ‘outputs’. Using the material itself as the active player in the decision making process offers possibilities for creating entirely soft devices that respond locally to environmental interactions or act as embedded sensors for feedback loops.