2024-06-25 パデュー大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.purdue.edu/newsroom/releases/2024/Q2/engineers-develop-faster-more-accurate-ai-algorithm-for-improving-nuclear-reactor-performance.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-43325-1
原子炉過渡現象予測のための領域類似性尺度に基づく転移学習付き物理情報ニューラルネットワーク(TL-PINN) Physics-informed neural network with transfer learning (TL-PINN) based on domain similarity measure for prediction of nuclear reactor transients
Konstantinos Prantikos,Stylianos Chatzidakis,Lefteri H. Tsoukalas & Alexander Heifetz
Scientific Reports Published:06 October 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-43325-1
Abstract
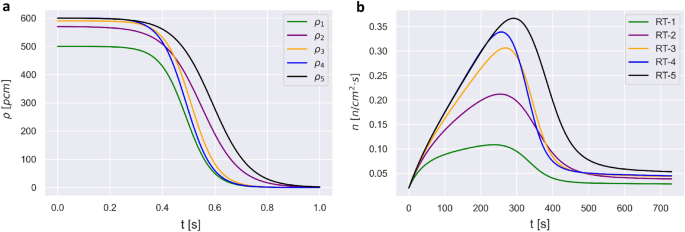
Nuclear reactor safety and efficiency can be enhanced through the development of accurate and fast methods for prediction of reactor transient (RT) states. Physics informed neural networks (PINNs) leverage deep learning methods to provide an alternative approach to RT modeling. Applications of PINNs in monitoring of RTs for operator support requires near real-time model performance. However, as with all machine learning models, development of a PINN involves time-consuming model training. Here, we show that a transfer learning (TL-PINN) approach achieves significant performance gain, as measured by reduction of the number of iterations for model training. Using point kinetic equations (PKEs) model with six neutron precursor groups, constructed with experimental parameters of the Purdue University Reactor One (PUR-1) research reactor, we generated different RTs with experimentally relevant range of variables. The RTs were characterized using Hausdorff and Fréchet distance. We have demonstrated that pre-training TL-PINN on one RT results in up to two orders of magnitude acceleration in prediction of a different RT. The mean error for conventional PINN and TL-PINN models prediction of neutron densities is smaller than 1%. We have developed a correlation between TL-PINN performance acceleration and similarity measure of RTs, which can be used as a guide for application of TL-PINNs.