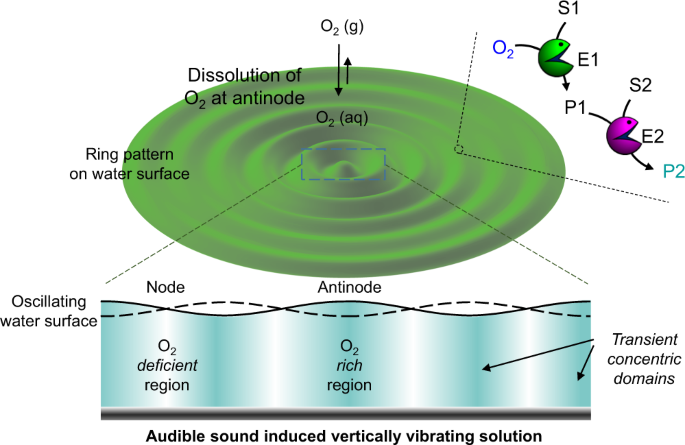
可聴音によって生成された無拘束の区分けにより、酵素反応を時空間的に制御することが可能になった Unhackneyed compartmentalization generated by audible sound allows the enzyme reactions to be controlled spatiotemporally
2022-05-02 大韓民国・基礎科学研究院(IBS)
<関連情報>
- https://www.ibs.re.kr/cop/bbs/BBSMSTR_000000000738/selectBoardArticle.do?nttId=21273&pageIndex=1&searchCnd=&searchWrd=
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-30124-x
可聴音によって誘起される溶液中の過渡領域におけるカスケード反応ネットワーク Cascade reaction networks within audible sound induced transient domains in a solution
Prabhu Dhasaiyan,Tanwistha Ghosh,Hong-Guen Lee,Yeonsang Lee,Ilha Hwang,Rahul Dev Mukhopadhyay,Kyeng Min Park,Seungwon Shin,In Seok Kang &Kimoon Kim
Nature Communications Published: 02 May 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30124-x
Abstract
Spatiotemporal control of chemical cascade reactions within compartmentalized domains is one of the difficult challenges to achieve. To implement such control, scientists have been working on the development of various artificial compartmentalized systems such as liposomes, vesicles, polymersomes, etc. Although a considerable amount of progress has been made in this direction, one still needs to develop alternative strategies for controlling cascade reaction networks within spatiotemporally controlled domains in a solution, which remains a non-trivial issue. Herein, we present the utilization of audible sound induced liquid vibrations for the generation of transient domains in an aqueous medium, which can be used for the control of cascade chemical reactions in a spatiotemporal fashion. This approach gives us access to highly reproducible spatiotemporal chemical gradients and patterns, in situ growth and aggregation of gold nanoparticles at predetermined locations or domains formed in a solution. Our strategy also gives us access to nanoparticle patterned hydrogels and their applications for region specific cell growth.